Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A sound wave is passing through air column in the form of compression and rarefaction. In consecutive compressions and rarefactions ______.
विकल्प
density remains constant.
Boyle’s law is obeyed.
bulk modulus of air oscillates.
there is no transfer of heat.
उत्तर
A sound wave is passing through air column in the form of compression and rarefaction. In consecutive compressions and rarefactions there is no transfer of heat.
Explanation:
- Due to compression and rarefactions density of the medium (air) changes. At compressed regions density is maximum and at rarefactions density is minimum.
- As density is changing, so Boyle's law is not obeyed.
- The bulk modulus remains the same.
- The time of compression and rarefaction is too small i.e. we can assume an adiabatic process and hence no transfer of heat.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A bat emits an ultrasonic sound of frequency 1000 kHz in the air. If the sound meets a water surface, what is the wavelength of the transmitted sound? The speed of sound in air is 340 m s–1 and in water 1486 m s–1.
Two strings A and B, made of same material, are stretched by same tension. The radius of string A is double of the radius of B. A transverse wave travels on A with speed `v_A` and on B with speed `v_B`. The ratio `v_A/v_B` is ______.
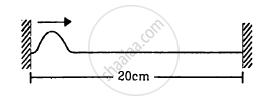
A string of length 20 cm and linear mass density 0⋅40 g cm−1 is fixed at both ends and is kept under a tension of 16 N. A wave pulse is produced at t = 0 near an ends as shown in the figure, which travels towards the other end. (a) When will the string have the shape shown in the figure again? (b) Sketch the shape of the string at a time half of that found in part (a).
Two waves, travelling in the same direction through the same region, have equal frequencies, wavelengths and amplitudes. If the amplitude of each wave is 4 mm and the phase difference between the waves is 90°, what is the resultant amplitude?
A 40 cm wire having a mass of 3⋅2 g is stretched between two fixed supports 40⋅05 cm apart. In its fundamental mode, the wire vibrates at 220 Hz. If the area of cross section of the wire is 1⋅0 mm2, find its Young modulus.
Use the formula `v = sqrt((gamma P)/rho)` to explain why the speed of sound in air increases with temperature.
Sound waves of wavelength λ travelling in a medium with a speed of v m/s enter into another medium where its speed is 2v m/s. Wavelength of sound waves in the second medium is ______.
At what temperatures (in °C) will the speed of sound in air be 3 times its value at O°C?
If c is r.m.s. speed of molecules in a gas and v is the speed of sound waves in the gas, show that c/v is constant and independent of temperature for all diatomic gases.
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement of an elastic wave.
- y = 5 cos (4x) sin (20t)
- y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2)
- y = 10 cos [(252 – 250) πt] cos [(252 + 250)πt]
- y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x)
State which of these represent
- a travelling wave along –x direction
- a stationary wave
- beats
- a travelling wave along +x direction.
Given reasons for your answers.
