Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
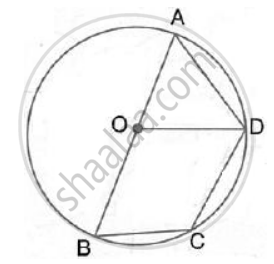
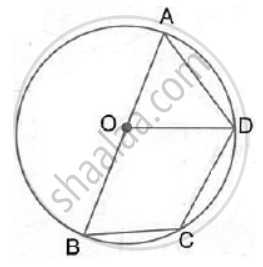
AB is the diameter of the circle with centre O. OD is parallel to BC and ∠ AOD = 60° ; calculate the numerical values of: ∠ ADC
उत्तर
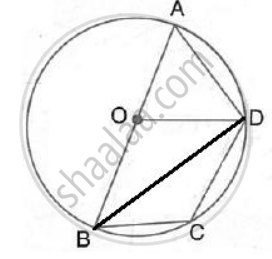
∠ABC = ∠ABD + ∠DBC = 30° + 30° = 60°
In cyclic quadrilateral ABCD,
∠ADC = 180° - ABC = 180° - 60° = 120°
(pair of opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
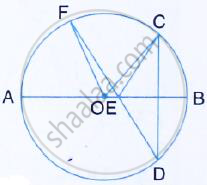
In the figure given below, AB is diameter of the circle whose centre is O. given that: ∠ECD =
∠EDC = 32°. Show that ∠COF = ∠CEF.
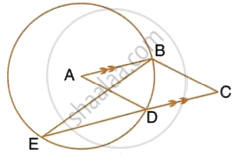
In the given figure, A is the centre of the circle, ABCD is a parallelogram and CDE is a straight line. Prove that : ∠BCD = 2∠ABE.
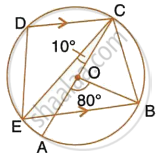
In the given figure, AC is the diameter of the circle with centre O. CD and BE are parallel. Angle ∠AOB = 80° and ∠ACE = 10°.
Calculate:
- Angle BEC,
- Angle BCD,
- Angle CED.
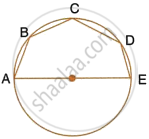
In the given figure, AE is the diameter of the circle. Write down the numerical value of ∠ABC + ∠CDE. Give reasons for your answer.
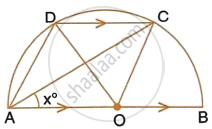
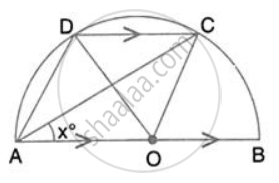
In the given figure, AOB is a diameter and DC is parallel to AB. If ∠CAB = x°; find (in terms of x) the values of :
- ∠COB,
- ∠DOC,
- ∠DAC,
- ∠ADC.
In the given figure, BD is a side of a regular hexagon, DC is a side of a regular pentagon and AD is a diameter.
Calculate :
- ∠ADC,
- ∠BDA,
- ∠ABC,
- ∠AEC.

In the given figure, AB is the diameter of the circle with centre O.
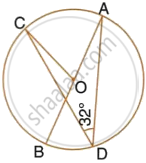
If ∠ADC = 32°, find angle BOC.
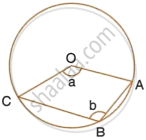
The figure given below, shows a circle with centre O. Given : ∠AOC = a and ∠ABC = b.
-
Find the relationship between a and b.
-
Find the measure of angle OAB, if OABC is a parallelogram.
In the given figure, AOB is a diameter and DC is parallel to AB. If ∠ CAB = xo ; find (in terms of x) the values of: ∠ DAC
AB is the diameter of the circle with centre O. OD is parallel to BC and ∠ AOD = 60° ; calculate the numerical values of: ∠ DBC