Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An isolated metal sphere is heated to a high temperature. Will it become positively charged due to thermionic emission?
उत्तर
Yes, it will become positively charged due to thermionic emission. When the metal sphere is heated, average kinetic energy of the electrons will increases, due to which, the free electrons of the metal sphere will be able to escape. As a result, they will leave a positive charge on the isolated metal sphere.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the maximum frequency of X-rays produced by 30 kV electrons.
Quarks inside protons and neutrons are thought to carry fractional charges [(+2/3)e; (–1/3)e]. Why do they not show up in Millikan’s oil-drop experiment?
The work function of the following metals is given : Na 2.75 ev, K = 2.3 eV, Mo = 4.17 eV and Ni = 5.15 eV. Which of these metals will not cause photoelectric emission for radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a laser source placed 1 m away from these metals? What happens if the laser source is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away?
Would you prefer a material with a high melting point or a low melting point to be used as a cathode in a diode?
Would you prefer a material with a high work-function or a low work-function to be used as a cathode in a diode?
A diode value is connected to a battery and a load resistance. The filament is heated, so that a constant current is obtained in the circuit. As the cathode continuously emits electrons, does it become more and more positively charged?
Why does thermionic emission not take place in non-conductors?
The cathode of a diode valve is replaced by another cathode of double the surface area. Keeping the voltage and temperature conditions the same, will the place current decrease, increase or remain the same?
The constant A in the Richardson−Dushman equation for tungsten is 60 × 104 A m−2K−2. The work function of tungsten is 4.5 eV. A tungsten cathode with a surface area 2.0 × 10−5 m2 is heated by a 24 W electric heater. In steady state, the heat radiated by the heater and the cathode equals the energy input by the heater and the temperature becomes constant. Assuming that the cathode radiates like a blackbody, calculate the saturation current due to thermions. Take Stefan's Constant = 6 × 10−8 W m−2 K−1. Assume that the thermions take only a small fraction of the heat supplied.
Answer the following question.
Define the term "Threshold frequency", in the context of photoelectric emission.
The wavelength λe of an electron and λp of a photon of same energy E are related by
The wave associated with a moving particle of mass 3 × 10–6 g has the same wavelength as an electron moving with a velocity 6 × 106 ms–1. The velocity of the particle is
Define the work function of a metal. Give its unit.
Consider Figure for photoemission.
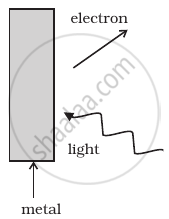
How would you reconcile with momentum conservation? Note light (photons) have momentum in a different direction than the emitted electrons.
Give an example each of a metal from which photoelectric emission takes place when irradiated by
- UV light
- visible light.
Name the factors on which photoelectric emission from a surface depends.
