Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An oil company has two depots, A and B, with capacities of 7000 litres and 4000 litres respectively. The company is to supply oil to three petrol pumps, D, E, F whose requirements are 4500, 3000 and 3500 litres respectively. The distance (in km) between the depots and petrol pumps is given in the following table:
Figure
Assuming that the transportation cost per km is Rs 1.00 per litre, how should the delivery be scheduled in order that the transportation cost is minimum?
उत्तर
Let x and y litres of oil be supplied from A to the petrol pumps D and E. Then, (7000 − x − y) L will be supplied from A to petrol pump F.
The requirement at petrol pump D is 4500 L. Since, x L are transported from depot A, the remaining (4500 −x) L will be transported from petrol pump B.
Similarly, (3000 − y) L and [3500 − (7000 − x − y)] L i.e. (x + y − 3500) L will be transported from depot B to petrol pump E and F. respectively.
The given problem can be represented diagrammatically as follows. 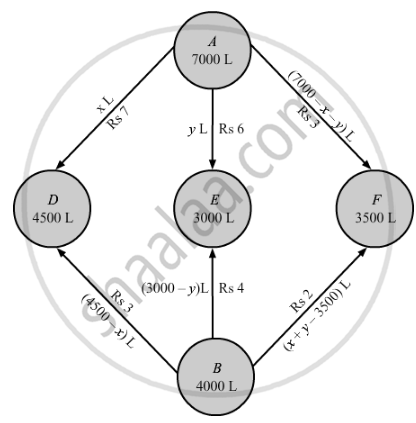
Since, quantity of oil are non-negative quantities.Therefore,
x ≥0 , y ≥ 0, and (7000 - x - y ) ≥ 0
⇒ x ≥ 0 , y ≥ 0, and x + y ≥ 7000
4500 - x ≥ 0 , 3000 - y ≥ 0 , and x + y -3500 ≥ 0
⇒ x ≤ 4500, y ≤ 3000, and x + y ≥ 3500
Cost of transporting 10 L of petrol = Re 1
Cost of transporting 1 L of petrol = \[Rs \frac{1}{10}\]
Therefore, total transportation cost is given by,
`z = 7/10 xx x+6/10 y + 3/10 (7000 - x -y ) + 3/10 (4500 - x) + 4/10 ( 3000 - y ) + 2/10( x + y - 3500)`
= 0.3x + 0.1y + 3950
The problem can be formulated as follows.
Minimize Z = 0.3x + 0.1y + 3950
subject to the constraints,
\[x + y \leq 7000\]
\[x \leq 4500\]
\[y \leq 3000\]
\[x + y \geq 3500\]
\[x, y \geq 0\]
First we will convert inequations into equations as follows:
x + y = 7000, x = 4500, y = 3000, x + y = 3500, x = 0 and y = 0
Region represented by x + y ≤ 7000:
The line x + y = 7000 meets the coordinate axes at A1(7000, 0) and \[B_1 \left( 0, 7000 \right)\] respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line x + y = 7000 . Clearly (0,0) satisfies the x + y = 7000 . So, the region which contains the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x + y ≤ 7000.
Region represented by x ≤ 4500:
The line x = 4500 is the line passes through C1(4500, 0) and is parallel to Y axis. The region to the left of the line x = 4500 will satisfy the inequation
x ≤ 4500.
Region represented by y ≤ 3000:
The line y = 3000 is the line passes through D1(0, 3000) and is parallel to X axis. The region below the the line y = 3000 will satisfy the inequation
y ≤ 3000.
Region represented by x + y ≥ 3500:
The line x + y = 7000 meets the coordinate axes at E1(3500, 0) and \[F_1 \left( 0, 3500 \right)\] respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line
x + y = 3500 . Clearly (0,0) satisfies the x + y = 3500. So, the region which contains the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x + y ≥ 3500.
Region represented by x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0:
Since, every point in the first quadrant satisfies these inequations. So, the first quadrant is the region represented by the inequations x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0.
The feasible region determined by the system of constraints x + y ≤ 7000, x ≤ 4500, y ≤ 3000, x + y ≥ 3500, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 are as follows.
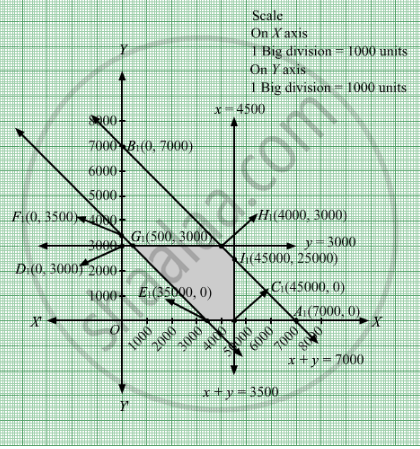
The corner points of the feasible region are E1(3500, 0), C1(4500, 0), I1(4500, 2500), H1(4000, 3000), and G1(500, 3000).
The values of Z at these corner points are as follows.
| Corner point | Z = 0.3x + 0.1y + 3950 |
| E1(3500, 0) | 5000 |
| C1(4500, 0) | 5300 |
| I1(4500, 2500) | 5550 |
| H1(4000, 3000) | 5450 |
| G1(500, 3000) | 4400 |
The minimum value of Z is 4400 at G1(500, 3000).
Thus, the oil supplied from depot A is 500 L, 3000 L, and 3500 L and from depot B is 4000 L, 0 L, and 0 L to petrol pumps D, E, and F respectively.
The minimum transportation cost is Rs 4400.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Solve the following L.P.P graphically:
Maximize: Z = 10x + 25y
Subject to: x ≤ 3, y ≤ 3, x + y ≤ 5, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize: z = 3x + 5y
Subject to: x + 4y ≤ 24
3x + y ≤ 21
x + y ≤ 9
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
A dietician wishes to mix two kinds ·of food X· and Y in such a way that the mixture contains at least 10 units of vitamin A, 12 units of vitamin B arid 8 units of vitamin C. The vitamin contents of one kg food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin.B | Vitamin C |
| X | 1 unit | 2 unit | 3 unit |
| Y | 2 unit | 2 unit | 1 unit |
Orie kg of food X costs Rs 24 and one kg of food Y costs Rs 36. Using Linear Programming, find the least cost of the total mixture. which will contain the required vitamins.
Maximize Z = 9x + 3y
Subject to
\[2x + 3y \leq 13\]
\[ 3x + y \leq 5\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 18x + 10y
Subject to
\[4x + y \geq 20\]
\[2x + 3y \geq 30\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 50x + 30y
Subject to
\[2x + y \leq 18\]
\[3x + 2y \leq 34\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x + 5y
Subject to
\[x + 2y \leq 20\]
\[x + y \leq 15\]
\[ y \leq 5\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = x + y
Subject to
\[- 2x + y \leq 1\]
\[ x \leq 2\]
\[ x + y \leq 3\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x1 + 4x2, if possible,
Subject to the constraints
\[x_1 - x_2 \leq - 1\]
\[ - x_1 + x_2 \leq 0\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Minimize z = 6 x + 3 y
Subject to the constraints:
4 x + \[y \geq\] 80
x + 5 \[y \geq\] 115
3 x + 2 \[y \leq\] 150
\[x \geq\] 0 , \[y \geq\] 0
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food P and Q in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contains at least 8 units of vitamin A and 11 units of vitamin B. Food P costs ₹60/kg and food Q costs ₹80/kg. Food P contains 3 units/kg of vitamin A and 5 units/kg of vitamin B while food Q contains 4 units/kg of vitamin A and 2 units/kg of vitamin B. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
A small manufacturer has employed 5 skilled men and 10 semi-skilled men and makes an article in two qualities deluxe model and an ordinary model. The making of a deluxe model requires 2 hrs. work by a skilled man and 2 hrs. work by a semi-skilled man. The ordinary model requires 1 hr by a skilled man and 3 hrs. by a semi-skilled man. By union rules no man may work more than 8 hrs per day. The manufacturers clear profit on deluxe model is Rs 15 and on an ordinary model is Rs 10. How many of each type should be made in order to maximize his total daily profit.
A factory owner purchases two types of machines, A and B, for his factory. The requirements and limitations for the machines are as follows:
| Area occupied by the machine |
Labour force for each machine |
Daily output in units |
|
| Machine A Machine B |
1000 sq. m 1200 sq. m |
12 men 8 men |
60 40 |
He has an area of 7600 sq. m available and 72 skilled men who can operate the machines.
How many machines of each type should he buy to maximize the daily output?
A manufacturer of Furniture makes two products : chairs and tables. processing of these products is done on two machines A and B. A chair requires 2 hrs on machine A and 6 hrs on machine B. A table requires 4 hrs on machine A and 2 hrs on machine B. There are 16 hrs of time per day available on machine A and 30 hrs on machine B. Profit gained by the manufacturer from a chair and a table is Rs 3 and Rs 5 respectively. Find with the help of graph what should be the daily production of each of the two products so as to maximize his profit.
A gardener has supply of fertilizer of type I which consists of 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and type II fertilizer which consists of 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, he finds that he needs at least 14 kg of nitrogen and 14 kg of phosphoric acid for his crop. If the type I fertilizer costs 60 paise per kg and type II fertilizer costs 40 paise per kg, determine how many kilograms of each fertilizer should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
A man owns a field of area 1000 sq.m. He wants to plant fruit trees in it. He has a sum of Rs 1400 to purchase young trees. He has the choice of two types of trees. Type A requires 10 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 20 per tree and type B requires 20 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 25 per tree. When fully grown, type A produces an average of 20 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs 2.00 per kg and type B produces an average of 40 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs. 1.50 per kg. How many of each type should be planted to achieve maximum profit when the trees are fully grown? What is the maximum profit?
A manufacturing company makes two models A and B of a product. Each piece of model A requires 9 labour hours for fabricating and 1 labour hour for finishing. Each piece of model B requires 12 labour hours for fabricating and 3 labour hours for finishing. For fabricating and finishing, the maximum labour hours available are 180 and 30 respectively. The company makes a profit of ₹8000 on each piece of model A and ₹12000 on each piece of model B. How many pieces of model A and model B should be manufactured per week to realise a maximum profit? What is the maximum profit per week?
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes 1.5 hours of machine time and 3 hours of craftman's time in its making while a cricket bat takes 3 hours of machine time and 1 hour of craftman's time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than 42 hours of machine time and 24 hours of craftman's time.
(i) What number of rackets and bats must be made if the factory is to work at full capacity?
(ii) If the profit on a racket and on a bat is Rs 20 and Rs 10 respectively, find the maximum profit of the factory when it works at full capacity.
There are two types of fertilizers F1 and F2. F1 consists of 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and F2 consists of 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, a farmer finds the she needs atleast 14 kg of nitrogen and 14 kg of phosphoric acid for her crop. If F1 costs ₹6/kg and F2 costs ₹5/kg, determine how much of each type of fertilizer should be used so that the nutrient requirements are met at minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
There are two types of fertilisers 'A' and 'B' . 'A' consists of 12% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid whereas 'B' consists of 4% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, farmer finds that he needs at least 12 kg of nitrogen and 12 kg of phosphoric acid for his crops. If 'A' costs ₹10 per kg and 'B' cost ₹8 per kg, then graphically determine how much of each type of fertiliser should be used so that nutrient requiremnets are met at a minimum cost
Tow godowns, A and B, have grain storage capacity of 100 quintals and 50 quintals respectively. They supply to 3 ration shops, D, E and F, whose requirements are 60, 50 and 40 quintals respectively. The cost of transportation per quintal from the godowns to the shops are given in the following table:
| Transportation cost per quintal(in Rs.) | ||
| From-> | A | B |
| To | ||
| D | 6.00 | 4.00 |
| E | 3.00 | 2.00 |
| F | 2.50 | 3.00 |
How should the supplies be transported in order that the transportation cost is minimum?
Maximize: z = 3x + 5y Subject to
x +4y ≤ 24 3x + y ≤ 21
x + y ≤ 9 x ≥ 0 , y ≥0
A carpenter has 90, 80 and 50 running feet respectively of teak wood, plywood and rosewood which is used to product A and product B. Each unit of product A requires 2, 1 and 1 running feet and each unit of product B requires 1, 2 and 1 running feet of teak wood, plywood and rosewood respectively. If product A is sold for Rs. 48 per unit and product B is sold for Rs. 40 per unit, how many units of product A and product B should be produced and sold by the carpenter, in order to obtain the maximum gross income? Formulate the above as a Linear Programming Problem and solve it, indicating clearly the feasible region in the graph.
A company manufactures two types of cardigans: type A and type B. It costs ₹ 360 to make a type A cardigan and ₹ 120 to make a type B cardigan. The company can make at most 300 cardigans and spend at most ₹ 72000 a day. The number of cardigans of type B cannot exceed the number of cardigans of type A by more than 200. The company makes a profit of ₹ 100 for each cardigan of type A and ₹ 50 for every cardigan of type B.
Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem to maximize the profit to the company. Solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
The graph of the inequality 3X − 4Y ≤ 12, X ≤ 1, X ≥ 0, Y ≥ 0 lies in fully in
Maximum value of 4x + 13y subject to constraints x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, x + y ≤ 5 and 3x + y ≤ 9 is ______.
Area of the region bounded by y = cos x, x = 0, x = π and X-axis is ______ sq.units.
For the function z = 19x + 9y to be maximum under the constraints 2x + 3y ≤ 134, x + 5y ≤ 200, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0; the values of x and y are ______.
For the LPP, maximize z = x + 4y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 2, x + 2y ≥ 8, x, y ≥ 0 ______.
Let R be the feasible region (convex polygon) for a linear programming problem and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. When Z has an optimal value (maximum or minimum), where the variables x and y are subject to constraints described by linear inequalities,
In Corner point method for solving a linear programming problem the first step is to ____________.
The constraints –x1 + x2 ≤ 1, –x1 + 3x2 ≤ 9, x1x2 ≥ 0 define on ______.
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Maximize: Z = x + 2y
Subject to constraints:
x + 2y ≥ 100,
2x – y ≤ 0
2x + y ≤ 200,
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize: P = 70x + 40y
Subject to: 3x + 2y ≤ 9,
3x + y ≤ 9,
x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0.
Aman has ₹ 1500 to purchase rice and wheat for his grocery shop. Each sack of rice and wheat costs ₹ 180 and Rupee ₹ 120 respectively. He can store a maximum number of 10 bags in his shop. He will earn a profit of ₹ 11 per bag of rice and ₹ 9 per bag of wheat.
- Formulate a Linear Programming Problem to maximise Aman’s profit.
- Calculate the maximum profit.
