Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Tow godowns, A and B, have grain storage capacity of 100 quintals and 50 quintals respectively. They supply to 3 ration shops, D, E and F, whose requirements are 60, 50 and 40 quintals respectively. The cost of transportation per quintal from the godowns to the shops are given in the following table:
| Transportation cost per quintal(in Rs.) | ||
| From-> | A | B |
| To | ||
| D | 6.00 | 4.00 |
| E | 3.00 | 2.00 |
| F | 2.50 | 3.00 |
How should the supplies be transported in order that the transportation cost is minimum?
उत्तर
Let godown A supply x quintals and y quintals of grain to the shops D and E respectively.
Then, (100 − x − y) will be supplied to shop F.
The requirement at shop D is 60 quintals since, x quintals are transported from godown A.
Therefore, the remaining (60 − x) quintals will be transported from godown B.
Similarly, (50 − y) quintals and 40 − (100 − x − y) i.e. (x + y − 60) quintals will be transported from godown B to shop E and F respectively.
The given problem can be represented diagrammatically as follows.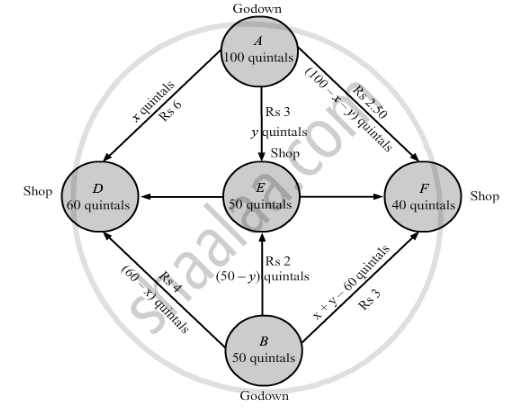
Quantity of the grain cannot be negative.Therefore,
x ≥ 0 , y ≥ 0 and 100 - x - y ≥ 0
⇒ x ≥ 0 , y ≥ 0 , and x + y ≤ 100
60 - x ≥ 0 , 50 - y ≥ 0 , and x + y - 60 ≥ 0
⇒ x ≤ 60 , y ≤ 50 , and x + y ≥ 60
Total transportation cost Z is given by,
\[Z = 6x + 3y + 2 . 5\left( 100 - x - y \right) + 4\left( 60 - x \right) + 2\left( 50 - y \right) + 3\left( x + y - 60 \right)\]
\[ = 6x + 3y + 250 - 2 . 5x - 2 . 5y + 240 - 4x + 100 - 2y + 3x + 3y - 180\]
\[ = 2 . 5x + 1 . 5y + 410\]
The given problem can be formulated as:
Minimize Z = 2.5x + 1.5y + 410
subject to the constraints,
\[x + y \leq 100\]
\[x \leq 60\]
\[y \leq 50\]
\[x + y \geq 60\]
\[x, y \geq 0\]
First we will convert inequations into equations as follows:
x + y = 100, x = 60, y = 50, x + y =60, x = 0 and y = 0
Region represented by x + y ≤ 100:
The line x + y = 100 meets the coordinate axes at A1(100, 0) and B1(0, 100) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line x + y = 100. Clearly (0,0) satisfies the x + y = 100. So, the region which contains the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x + y ≤ 100.
Region represented by x ≤ 60:
x = 60 is the line that passes (60, 0) and is parallel to the Y axis.The region to the left of the line x = 60 will satisfy the inequation x ≤ 60.
Region represented by y ≤ 50:
y = 50 is the line that passes (0, 50) and is parallel to the X axis.The region below the line y = 50 will satisfy the inequation y ≤ 50.
Region represented by x + y ≥ 60:
The line x + y = 60 meets the coordinate axes at C1(60, 0) and \[D_1 \left( 0, 60 \right)\] respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line x + y = 60. Clearly (0,0) does not satisfies the inequation x + y ≥ 60. So,the region which does not contain the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x + y ≥ 60.
Region represented by x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0:
Since, every point in the first quadrant satisfies these inequations. So, the first quadrant is the region represented by the inequations x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0.
The feasible region determined by the system of constraints x + y ≤ 100, x ≤ 60, y ≤ 50, x + y ≥ 60, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 are as follows.
The corner points are C1(60, 0), G1(60, 40), F1(50, 50), and E1(10, 50).
The values of Z at these corner points are as follows.
| Corner point | Z = 2.5x + 1.5y + 410 |
| C1(60, 0) | 560 |
| G1(60, 40) | 620 |
| F1(50, 50) | 610 |
| E1(10, 50) | 510 |
The minimum value of Z is 510 at E1(10, 50).
Thus, the amount of grain transported from A to D, E, and F is 10 quintals, 50 quintals, and 40 quintals respectively and from B to D, E, and F is 50 quintals, 0 quintals, and 0 quintals respectively.
The minimum cost is Rs 510.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A retired person wants to invest an amount of Rs. 50, 000. His broker recommends investing in two type of bonds ‘A’ and ‘B’ yielding 10% and 9% return respectively on the invested amount. He decides to invest at least Rs. 20,000 in bond ‘A’ and at least Rs. 10,000 in bond ‘B’. He also wants to invest at least as much in bond ‘A’ as in bond ‘B’. Solve this linear programming problem graphically to maximise his returns.
Solve the following L.P.P. graphically Maximise Z = 4x + y
Subject to following constraints x + y ≤ 50
3x + y ≤ 90,
x ≥ 10
x, y ≥ 0
In order to supplement daily diet, a person wishes to take X and Y tablets. The contents (in milligrams per tablet) of iron, calcium and vitamins in X and Y are given as below :
| Tablets | Iron | Calcium | Vitamin |
| x | 6 | 3 | 2 |
| y | 2 | 3 | 4 |
The person needs to supplement at least 18 milligrams of iron, 21 milligrams of calcium and 16 milligrams of vitamins. The price of each tablet of X and Y is Rs 2 and Rs 1 respectively. How many tablets of each type should the person take in order to satisfy the above requirement at the minimum cost? Make an LPP and solve graphically.
Maximise z = 8x + 9y subject to the constraints given below :
2x + 3y ≤ 6
3x − 2y ≤6
y ≤ 1
x, y ≥ 0
Maximize Z = 9x + 3y
Subject to
\[2x + 3y \leq 13\]
\[ 3x + y \leq 5\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 15x + 10y
Subject to
\[3x + 2y \leq 80\]
\[2x + 3y \leq 70\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 10x + 6y
Subject to
\[3x + y \leq 12\]
\[2x + 5y \leq 34\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 2x + 4y
Subject to
\[x + y \geq 8\]
\[x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[x \geq 3, y \geq 2\]
Maximize Z = 3x1 + 4x2, if possible,
Subject to the constraints
\[x_1 - x_2 \leq - 1\]
\[ - x_1 + x_2 \leq 0\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x + 3y, if possible,
Subject to the constraints
\[x - y \leq 1\]
\[x + y \geq 3\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Find the maximum and minimum value of 2x + y subject to the constraints:
x + 3y ≥ 6, x − 3y ≤ 3, 3x + 4y ≤ 24, − 3x + 2y ≤ 6, 5x + y ≥ 5, x, y ≥ 0.
A diet for a sick person must contain at least 4000 units of vitamins, 50 units of minerals and 1400 of calories. Two foods A and B, are available at a cost of Rs 4 and Rs 3 per unit respectively. If one unit of A contains 200 units of vitamin, 1 unit of mineral and 40 calories and one unit of food B contains 100 units of vitamin, 2 units of minerals and 40 calories, find what combination of foods should be used to have the least cost?
One kind of cake requires 200 g of flour and 25 g of fat, and another kind of cake requires 100 g of flour and 50 g of fat. Find the maximum number of cakes which can be made from 5 kg of flour and 1 kg of fat assuming that there is no storage of the other ingredients used in making the cakes.
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend Rs 2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to Rs 5/per km. He has Rs 100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
A small manufacturer has employed 5 skilled men and 10 semi-skilled men and makes an article in two qualities deluxe model and an ordinary model. The making of a deluxe model requires 2 hrs. work by a skilled man and 2 hrs. work by a semi-skilled man. The ordinary model requires 1 hr by a skilled man and 3 hrs. by a semi-skilled man. By union rules no man may work more than 8 hrs per day. The manufacturers clear profit on deluxe model is Rs 15 and on an ordinary model is Rs 10. How many of each type should be made in order to maximize his total daily profit.
A firm manufactures two products A and B. Each product is processed on two machines M1 and M2. Product A requires 4 minutes of processing time on M1 and 8 min. on M2 ; product B requires 4 minutes on M1 and 4 min. on M2. The machine M1 is available for not more than 8 hrs 20 min. while machine M2 is available for 10 hrs. during any working day. The products A and B are sold at a profit of Rs 3 and Rs 4 respectively.
Formulate the problem as a linear programming problem and find how many products of each type should be produced by the firm each day in order to get maximum profit.
A factory uses three different resources for the manufacture of two different products, 20 units of the resources A, 12 units of B and 16 units of C being available. 1 unit of the first product requires 2, 2 and 4 units of the respective resources and 1 unit of the second product requires 4, 2 and 0 units of respective resources. It is known that the first product gives a profit of 2 monetary units per unit and the second 3. Formulate the linear programming problem. How many units of each product should be manufactured for maximizing the profit? Solve it graphically.
A manufacturer of patent medicines is preparing a production plan on medicines, A and B. There are sufficient raw materials available to make 20000 bottles of A and 40000 bottles of B, but there are only 45000 bottles into which either of the medicines can be put. Further, it takes 3 hours to prepare enough material to fill 1000 bottles of A, it takes 1 hour to prepare enough material to fill 1000 bottles of B and there are 66 hours available for this operation. The profit is Rs 8 per bottle for A and Rs 7 per bottle for B. How should the manufacturer schedule his production in order to maximize his profit?
A man owns a field of area 1000 sq.m. He wants to plant fruit trees in it. He has a sum of Rs 1400 to purchase young trees. He has the choice of two types of trees. Type A requires 10 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 20 per tree and type B requires 20 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 25 per tree. When fully grown, type A produces an average of 20 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs 2.00 per kg and type B produces an average of 40 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs. 1.50 per kg. How many of each type should be planted to achieve maximum profit when the trees are fully grown? What is the maximum profit?
A cottage industry manufactures pedestal lamps and wooden shades, each requiring the use of grinding/cutting machine and sprayer. It takes 2 hours on the grinding/cutting machine and 3 hours on the sprayer to manufacture a pedestal lamp while it takes 1 hour on the grinding/cutting machine and 2 hours on the sprayer to manufacture a shade. On any day, the sprayer is available for at most 20 hours and the grinding/cutting machine for at most 12 hours. The profit from the sale of a lamp is ₹5.00 and a shade is ₹3.00. Assuming that the manufacturer sell all the lamps and shades that he produces, how should he schedule his daily production in order to maximise his profit?
A library has to accommodate two different types of books on a shelf. The books are 6 cm and 4 cm thick and weigh 1 kg and \[1\frac{1}{2}\] kg each respectively. The shelf is 96 cm long and atmost can support a weight of 21 kg. How should the shelf be filled with the books of two types in order to include the greatest number of books? Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes 1.5 hours of machine time and 3 hours of craftman's time in its making while a cricket bat takes 3 hours of machine time and 1 hour of craftman's time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than 42 hours of machine time and 24 hours of craftman's time. If the profit on a racket and on a bat is Rs 20 and Rs 10 respectively, find the number of tennis rackets and cricket bats that the factory must manufacture to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A manufacturer considers that men and women workers are equally efficient and so he pays them at the same rate. He has 30 and 17 units of workers (male and female) and capital respectively, which he uses to produce two types of goods A and B. To produce one unit of A, 2 workers and 3 units of capital are required while 3 workers and 1 unit of capital is required to produce one unit of B. If A and B are priced at ₹100 and ₹120 per unit respectively, how should he use his resources to maximise the total revenue? Form the above as an LPP and solve graphically. Do you agree with this view of the manufacturer that men and women workers are equally efficient and so should be paid at the same rate?
A medical company has factories at two places, A and B. From these places, supply is made to each of its three agencies situated at P, Q and R. The monthly requirements of the agencies are respectively 40, 40 and 50 packets of the medicines, while the production capacity of the factories, A and B, are 60 and 70 packets respectively. The transportation cost per packet from the factories to the agencies are given below:
| Transportation Cost per packet(in Rs.) | ||
| From-> | A | B |
| To | ||
| P | 5 | 4 |
| Q | 4 | 2 |
| R | 3 | 5 |
By graphical method, the solution of linear programming problem
\[\text{ Subject } to \text{ 3 } x_1 + 2 x_2 \leq 18\]
\[ x_1 \leq 4\]
\[ x_2 \leq 6\]
\[ x_1 \geq 0, x_2 \geq 0, \text{ is } \]
A company manufactures two types of cardigans: type A and type B. It costs ₹ 360 to make a type A cardigan and ₹ 120 to make a type B cardigan. The company can make at most 300 cardigans and spend at most ₹ 72000 a day. The number of cardigans of type B cannot exceed the number of cardigans of type A by more than 200. The company makes a profit of ₹ 100 for each cardigan of type A and ₹ 50 for every cardigan of type B.
Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem to maximize the profit to the company. Solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
For the LPP, maximize z = x + 4y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 2, x + 2y ≥ 8, x, y ≥ 0 ______.
The constraints of an LPP are 7 ≤ x ≤ 12, 8 ≤ y ≤ 13. Determine the vertices of the feasible region formed by them.
Of all the points of the feasible region for maximum or minimum of objective function the points.
A set of values of decision variables which satisfies the linear constraints and nn-negativity conditions of an L.P.P. is called its ____________.
Let R be the feasible region (convex polygon) for a linear programming problem and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. When Z has an optimal value (maximum or minimum), where the variables x and y are subject to constraints described by linear inequalities,
In the Corner point method for solving a linear programming problem the second step after finding the feasible region of the linear programming problem and determining its corner points is ____________.
The corner points of the bounded feasible region of a LPP are A(0,50), B(20, 40), C(50, 100) and D(0, 200) and the objective function is Z = x + 2y. Then the maximum value is ____________.
The comer point of the feasible region determined by the following system of linear inequalities:
2x + y ≤ 10, x + 3y ≤ 15, x, y ≥ 0 are (0, 0), (5, 0), (3, 4) and (0, 5). Let x = Px + qx where P, q > 0 condition on P and Q so that the maximum of z occurs at both (3, 4) and (0, 5) is
Minimise z = – 3x + 4y subject to x + 2y ≤ 8, 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 What will be the minimum value of z ?
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize Z = 400x + 300y subject to x + y ≤ 200, x ≤ 40, x ≥ 20, y ≥ 0
The maximum value of 2x + y subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26 and 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
Minimize z = x + 2y,
Subject to x + 2y ≥ 50, 2x – y ≤ 0, 2x + y ≤ 100, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
