Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer in brief:
What is meant by coherent sources?
What are coherent sources?
उत्तर १
Two sources which emit waves of the same frequency having a constant phase difference, independent of time, are called coherent sources.
उत्तर २
Two light sources are said to be coherent if they produce waves that have the same phase or constant phase difference, same frequency or wavelength (monochromatic), same waveform and preferably the same amplitude.
संबंधित प्रश्न
State any one difference between interference of light and diffraction of light
Laser light of wavelength 630 nm is incident on a pair of slits which are separated by 1.8 mm. If the screen is kept 80 cm away from the two slits, calculate:
1) fringe separation i.e. fringe width.
2) distance of 10th bright fringe from the centre of the interference pattern
When a drop of oil is spread on a water surface, it displays beautiful colours in daylight because of ______________ .
A long narrow horizontal slit is paced 1 mm above a horizontal plane mirror. The interference between the light coming directly from the slit and that after reflection is seen on a screen 1.0 m away from the slit. Find the fringe-width if the light used has a wavelength of 700 nm.
The intensity at the central maximum (O) in a Young’s double slit experimental set-up shown in the figure is IO. If the distance OP equals one-third of the fringe width of the pattern, show that the intensity at point P, would equal `(I_0)/4`.

Answer the following question.
Describe any two characteristic features which distinguish between interference and diffraction phenomena. Derive the expression for the intensity at a point of the interference pattern in Young's double-slit experiment.
Answer in brief:
Explain what is the optical path length. How is it different from actual path length?
Describe Young's double-slit interference experiment and derive conditions for occurrence of dark and bright fringes on the screen. Define fringe width and derive a formula for it.
A double-slit arrangement produces interference fringes for sodium light (λ = 589 nm) that are 0.20° apart. What is the angular fringe separation if the entire arrangement is immersed in water (n = 1.33)?
The intensity of the light coming from one of the slits in Young's experiment is twice the intensity of the light coming from the other slit. What will be the approximate ratio of the intensities of the bright and dark fringes in the resulting interference pattern?
Two coherent sources whose intensity ratio is 25:1 produce interference fringes. Calculate the ratio of amplitudes of light waves coming from them.
Why two light sources must be of equal intensity to obtain a well-defined interference pattern?
Draw a neat labelled ray diagram of the Fresnel Biprism experiment showing the region of interference.
In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the slit separation is doubled. To maintain the same fringe spacing on the screen, the screen-to-slit distance D must be changed to ______.
One of Young’s double slits is covered with a glass plate as shown in figure. The position of central maximum will,
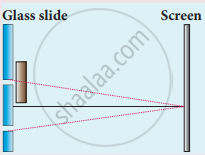
What is intensity (or) amplitude division?
Obtain the equation for resultant intensity due to interference of light.
In Young’s double slit experiment, the slits are 2 mm apart and are illuminated with a mixture of two wavelength λ0 = 750 nm and λ = 900 nm. What is the minimum distance from the common central bright fringe on a screen 2 m from the slits where a bright fringe from one interference pattern coincides with a bright fringe from the other?
Light of wavelength 600 nm that falls on a pair of slits producing interference pattern on a screen in which the bright fringes are separated by 7.2 mm. What must be the wavelength of another light which produces bright fringes separated by 8.1 mm with the same apparatus?
In Young's double-slit experiment, in an interference pattern, a second minimum is observed exactly in front of one slit. The distance between the two coherent sources is 'd' and the distance between source and screen is 'D'. The wavelength of the light source used is ______
A graph is plotted between the fringe-width Z and the distance D between the slit and eye-piece, keeping other adjustment same. The correct graph is
A.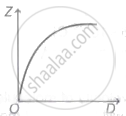 |
B. |
C.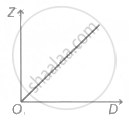 |
D.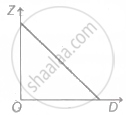 |
If the monochromatic source in Young's double slit experiment is white light, then ____________.
On a rainy day, a small oil film on water shows brilliant colours. This is due to ____________.
The distance between the first and ninth bright fringes formed in a biprism experiment is ______.
(`lambda` = 6000 A, D = 1.0 m, d = 1.2 mm)
Two identical light waves having phase difference 'Φ' propagate in same direction. When they superpose, the intensity of the resultant wave is proportional to ______.
In a Young's experiment, two coherent sources are placed 0.60 mm apart and the fringes are observed one metre away. If it produces the second dark fringe at a distance of 1 mm from the central fringe, the wavelength of monochromatic light used would be ____________.
In Young's double slit experiment fifth dark fringe is formed opposite to one of the slits. If D is the distance between the slits and the screen and d is the separation between the slits, then the wavelength of light used is ______.
The phenomenon of interference is based on ______.
Two sources of light 0.5 mm apart are placed at a distance of 2.4 m and wavelength of light is 5000 Å. The phase difference between the two light waves interfering on the screen at a point at a distance 3 mm from central bright band is ____________.
In biprism experiment, the 4th dark band is formed opposite to one of the slits. The wavelength of light used is ______.
In a double slit experiment, the separation between the slits is d and distance of screen from slits is D. If the wavelength of light used is `lambda` and I is the intensity of central bright fringe, then intensity at distance x from central maximum is given by ____________.
In a biprism experiment, the slit separation is 1 mm. Using monochromatic light of wavelength 5000 Å, an interference pattern is obtained on the screen. Where should the screen be moved? so that the change in fringe width is 12.5 x 105 m?
If two light waves reaching a point produce destructive interference, then the condition of phase difference is ______
In a biprism experiment, monochromatic light of wavelength (λ) is used. The distance between two coherent sources is kept constant. If the distance between slit and eyepiece (D) is varied as D1, D2, D3, and D4, the corresponding measured fringe widths are z1, z2, z3, and z4 then ______
Light waves from two coherent sources arrive at two points on a screen with a path difference of zero and λ/2. The ratio of the intensities at the points is ______
Two waves with same amplitude and frequency superpose at a point. The ratio of resultant intensities when they arrive in phase to that when they arrive 90° out of phase is ______.
`[cos pi/2=0]`
In Young's double-slit experiment, the distance between the slits is 3 mm and the slits are 2 m away from the screen. Two interference patterns can be obtained on the screen due to light of wavelength 480 nm and 600 run respectively. The separation on the screen between the 5th order bright fringes on the two interference patterns is ______
How will the interference pattern of Young's double slit change if one of the two slits is covered by a paper which transmits only half of the light intensity?
Interference fringes are produced on a screen by using two light sources of intensities I and 9I. The phase difference between the beams is `pi/2` at point P and π at point Q on the screen. The difference between the resultant intensities at point P and Q is ______.
