Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
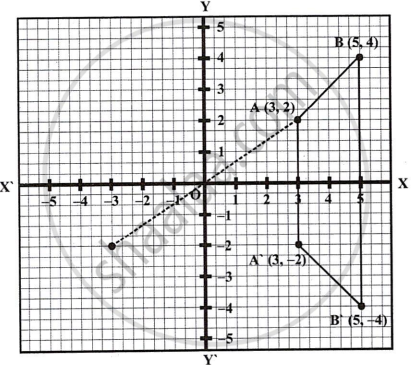
Attempt this question on graph paper.
- Plot A (3, 2) and B (5, 4) on graph paper. Take 2 cm = 1 unit on both the axes.
- Reflect A and B in the x-axis to A’ and B’ respectively. Plot these points also on the same graph paper.
- Write down:
- the geometrical name of the figure ABB’A’;
- the measure of angle ABB’;
- the image of A” of A, when A is reflected in the origin.
- the single transformation that maps A’ to A”.
उत्तर
- ∵ From the graph, we can say that
- ∵ Mx (x, y) = (x, –y)
Thus, Mx (3, 2) = (3, –2) and Mx (5, 4) = (5, –4) -
- an isosceles trapezium
- 45°
- ∵ Mo (x, y) = (–x, –y)
- Now A' (3, –2) `\implies` A" (–3, –2) ...[∵ My (x, y) = (–x, y)]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
- Point P (a, b) is reflected in the x-axis to P’ (5, –2). Write down the values of a and b.
- P” is the image of P when reflected in the y-axis. Write down the co-ordinates of P”.
- Name a single transformation that maps P’ to P”.
The point (–2, 0) on reflection in a line is mapped to (2, 0) and the point (5, –6) on reflection in the same line is mapped to (–5, –6).
- State the name of the mirror line and write its equation.
- State the co-ordinates of the image of (–8, –5) in the mirror line.
A point P (a, b) is reflected in the x-axis to P’ (2, –3). Write down the values of a and b. P” is the image of P, reflected in the y-axis. Write down the co-ordinates of P”. Find the co-ordinates of P”’, when P is reflected in the line, parallel to y-axis, such that x = 4.
- Plot the points A (3, 5) and B (–2, –4). Use 1 cm = 1 unit on both the axes.
- A’ is the image of A when reflected in the x-axis. Write down the co-ordinates of A’ and plot it on the graph paper.
- B’ is the image of B when reflected in the y-axis, followed by reflection in the origin. Write down the co-ordinates of B’ and plot it on the graph paper.
- Write down the geometrical name of the figure AA’BB’.
- Name the invariant points under reflection in the x-axis.
The point P (5, 3) was reflected in the origin to get the image P’.
- Write down the co-ordinates of P’.
- If M is the foot of the perpendicular from P to the x-axis, find the co-ordinates of M.
- If N is the foot of the perpendicular from P’ to the x-axis, find the co-ordinates of N.
- Name the figure PMP’N.
- Find the area of the figure PMP’N.
The point P (3, 4) is reflected to P’ in the x-axis; and O’ is the image of O (the origin) when reflected in the line PP’. Write:
- the co-ordinates of P’ and O’.
- the length of the segments PP’ and OO’.
- the perimeter of the quadrilateral POP’O’.
- the geometrical name of the figure POP’O’.
A (1, 1), B (5, 1), C (4, 2) and D (2, 2) are vertices of a quadrilateral. Name the quadrilateral ABCD. A, B, C, and D are reflected in the origin on to A’, B’, C’ and D’ respectively. Locate A’, B’, C’ and D’ on the graph sheet and write their co-ordinates. Are D, A, A’ and D’ collinear?
- The point P (2, –4) is reflected about the line x = 0 to get the image Q. Find the co-ordinates of Q.
- The point Q is reflected about the line y = 0 to get the image R. Find the co-ordinates of R.
- Name the figure PQR.
- Find the area of figure PQR.
A’ and B’ are images of A (-3, 5) and B (-5, 3) respectively on reflection in y-axis. Find: (
a) the co-ordinates of A’ and B’.
(b) Assign special name of quadrilateral AA’B’B.
(c) Are AB’ and BA’ equal in length?
Using a graph paper, plot the point A (6, 4) and B (0, 4).
(a) Reflect A and B in the origin to get the image A’ and B’.
(b) Write the co-ordinates of A’ and B’.
(c) Sate the geometrical name for the figure ABA’B’.
(d) Find its perimeter.
