Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Box I contains two white and three black balls. Box II contains four white and one black balls and box III contains three white ·and four black balls. A dice having three red, two yellow and one green face, is thrown to select the box. If red face turns up, we pick up the box I, if a yellow face turns up we pick up box II, otherwise, we pick up box III. Then, we draw a ball from the selected box. If the ball is drawn is white, what is the probability that the dice had turned up with a red face?
उत्तर
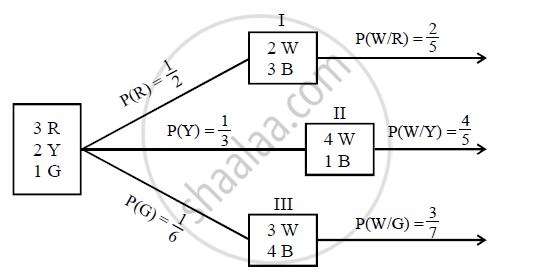
P(Total) = `1/2 xx 2/5 + 1/3 xx 4/5 + 1/6 xx 3/7`
`=1/5 + 4/15 + 1/14`
`= (42 + 56 + 15)/210`
`= 113/210`
`P(R"/"W) = (P(R).P(W"/"R))/"P(Total)"`
`= (1/2 xx 2/5)/(113/210)`
`= 1/5 xx 210/113`
`= 42/113`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A die is thrown three times. Events A and B are defined as below:
A : 5 on the first and 6 on the second throw.
B: 3 or 4 on the third throw.
Find the probability of B, given that A has already occurred.
Suppose that 80% of all families own a television set. If 5 families are interviewed at random, find the probability that
a. three families own a television set.
b. at least two families own a television set.
If `P(A) = 6/11, P(B) = 5/11 "and" P(A ∪ B) = 7/11` find
- P(A ∩ B)
- P(A|B)
- P(B|A)
Given that the two numbers appearing on throwing the two dice are different. Find the probability of the event ‘the sum of numbers on the dice is 4’.
If P(A) = `1/2`, P(B) = 0, then P(A|B) is ______.
A and B are two events such that P (A) ≠ 0. Find P (B|A), if A ∩ B = Φ.
In a game, a man wins a rupee for a six and loses a rupee for any other number when a fair die is thrown. The man decided to throw a die thrice but to quit as and when he gets a six. Find the expected value of the amount he wins/loses.
An urn contains 2 white and 2 black balls. A ball is drawn at random. If it is white, it is not replaced into the urn. Otherwise, it is replaced with another ball of the same colour. The process is repeated. Find the probability that the third ball is drawn is black.
Five dice are thrown simultaneously. If the occurrence of an odd number in a single dice is considered a success, find the probability of maximum three successes.
In an examination, 30% of students have failed in subject I, 20% of the students have failed in subject II and 10% have failed in both subject I and subject II. A student is selected at random, what is the probability that the student has failed in at least one subject?
From a pack of well-shuffled cards, two cards are drawn at random. Find the probability that both the cards are diamonds when first card drawn is kept aside
If A and B are two independent events such that P(A ∪ B) = 0.6, P(A) = 0.2, find P(B)
Given P(A) = 0.4 and P(A ∪ B) = 0.7 Find P(B) if A and B are independent events
Given P(A) = 0.4 and P(A ∪ B) = 0.7 Find P(B) if P(A/B) = 0.4
A die is thrown nine times. If getting an odd number is considered as a success, then the probability of three successes is ______
If X denotes the number of ones in five consecutive throws of a dice, then P(X = 4) is ______
Let A and B be two events. If P(A) = 0.2, P(B) = 0.4, P(A ∪ B) = 0.6, then P(A|B) is equal to ______.
If P(A ∩ B) = `7/10` and P(B) = `17/20`, then P(A|B) equals ______.
If P(A) = `3/10`, P(B) = `2/5` and P(A ∪ B) = `3/5`, then P(B|A) + P(A|B) equals ______.
If two balls are drawn from a bag containing 3 white, 4 black and 5 red balls. Then, the probability that the drawn balls are of different colours is:
A bag contains 6 red and 5 blue balls and another bag contains 5 red and 8 blue balls. A ball is drawn from the first bag and without noticing its colour is placed in the second bag. If a ball is drawn from the second bag, then find the probability that the drawn ball is red in colour.
For a biased dice, the probability for the different faces to turn up are
| Face | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| P | 0.10 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.17 |
The dice is tossed and it is told that either the face 1 or face 2 has shown up, then the probability that it is face 1, is ______.
Let A, B be two events such that the probability of A is `3/10` and conditional probability of A given B is `1/2`. The probability that exactly one of the events A or B happen equals.
It is given that the events A and B are such that P(A) = `1/4, P(A/B) = 1/2` and `P(B/A) = 2/3`, then P(B) is equal to ______.
If A and B are two independent events such that P(A) = `1/3` and P(B) = `1/4`, then `P(B^'/A)` is ______.
Compute P(A|B), if P(B) = 0.5 and P (A ∩ B) = 0.32.
