Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
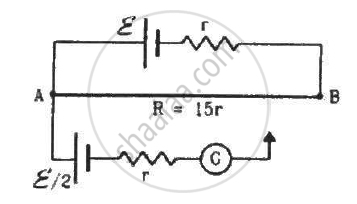
Consider the potentiometer circuit as arranged in the figure. The potentiometer wire is 600 cm long. (a) At what distance from the point A should the jockey touch the wire to get zero deflection in the galvanometer? (b) If the jockey touches the wire at a distance of 560 cm from A, what will be the current in the galvanometer?
उत्तर
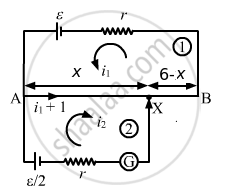
Let X be the null point on the wire at a distance x cm from point A, as shown.
Given:-
Total resistance of the wire AB = 15r
Resistance per unit cm = \[\frac{15r}{600}\]
Resistance of x cm of the wire = \[\frac{15rx}{600}\]
Resistance of (600 - x ) cm of the wire = \[\frac{15r\left( 600 - x \right)}{600}\]
(a) Applying KVL in loop 1, we get:-
\[\left( i_1 + i_2 \right)\frac{15}{600}rx + \frac{15}{600}r\left( 600 - x \right) i_1 + i_1 r = \epsilon...........(1)\]
Applying KVL in loop 2, we get:-
\[i_2 r + \frac{15}{600}rx \left( i_1 + i_2 \right) = \frac{\epsilon}{2}............(2)\]
For zero deflection in the galvanometer, i2 = 0. From equation (2),
\[\frac{15}{600}rx\left( i_1 \right) = \frac{\epsilon}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow i_1 = \frac{20\epsilon}{rx}\]
Substituting the values of i1 and i2 in equation (1), we get:-
x = 320 cm
(b) Putting x = 560 cm and solving equations (1) and (2), we get:-
\[i_2 = \frac{3\epsilon}{22r}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Kirchhoff's voltage law and current law are respectively in accordance with the conservation of .................................. .
- charge and momentum
- charge and energy
- energy and charge
- energy and momentum
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in electric networks. How are there rules justified?
Use Kirchhoff's rules to obtain conditions for the balance condition in a Wheatstone bridge.
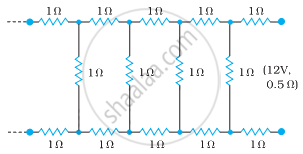
Determine the current drawn from a 12 V supply with internal resistance 0.5 Ω by the infinite network shown in the figure. Each resistor has 1 Ω resistance.
State Kirchhoff's rules for an electric network. Using Kirchhoff's rules, obtain the balance condition in terms of the resistances of four arms of Wheatstone bridge.
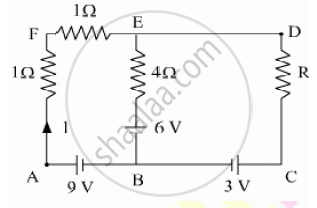
Using Kirchhoff’s rules determine the value of unknown resistance R in the circuit so that no current flows through 4 Ω resistance. Also find the potential difference between A and D.
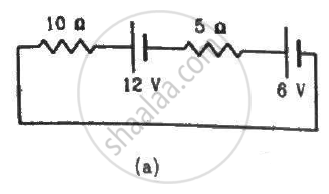
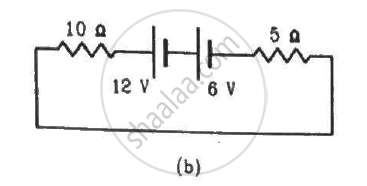
Consider the circuit shown in the figure. Find (a) the current in the circuit (b) the potential drop across the 5 Ω resistor (c) the potential drop across the 10 Ω resistor (d) Answer the parts (a), (b) and (c) with reference to the figure.
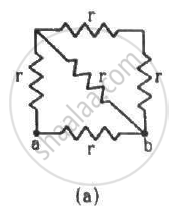
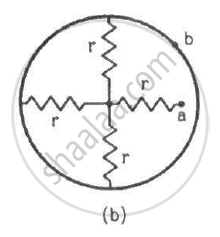
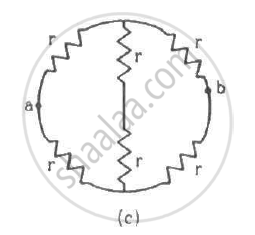
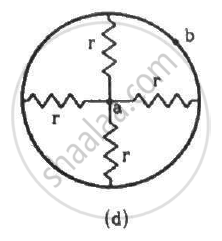
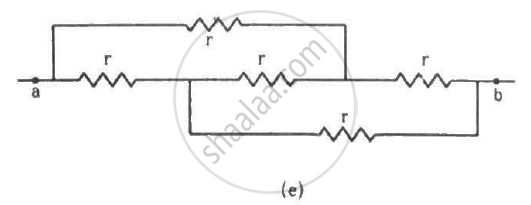
Find the equivalent resistances of the networks shown in the figure between the points a and b.
An infinite ladder is constructed with 1 Ω and 2 Ω resistors, as shown in the figure. (a) Find the effective resistance between the points A and B. (b) Find the current that passes through the 2 Ω resistor nearest to the battery.

Solve the following question.
Using Kirchhoff’s rules, calculate the current through the 40 Ω and 20 Ω resistors in the following circuit.

State the principle of potentiometer.
A potentiometer wire has a length of 4 m and resistance of 20 Ω. It is connected in series with resistance of 2980 Ω and a cell of emf 4 V. Calculate the potential along the wire.
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of emf 1.25 V gives a balance point at 35 cm length of the wire. If the cell is replaced by another cell and the balance point shifts to 63 cm, what is the emf of the second cell?
The Kirchhoff's second law (ΣiR = ΣE), where the symbols have their usual meanings, is based on ______.
What are the advantages of the null-point method in a Wheatstone bridge? What additional measurements would be required to calculate `R_(unknown)` by any other method?
What is the advantage of using thick metallic strips to join wires in a potentiometer?
Power P is to be delivered to a device via transmission cables having resistance RC. If V is the voltage across R and I the current through it, find the power wasted and how can it be reduced.
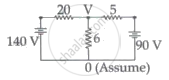
The value of current in the 6Ω resistance is ______.
The figure below shows two batteries, E1 and E2, having emfs of 18V and 10V and internal resistances of 1 Ω and 2 Ω, respectively. W1, W2 and W3 are uniform metallic wires AC, FD and BE having resistances of 8 Ω, 6 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. B and E are midpoints of the wires W1 and W2. Using Kirchhoff's laws of electrical circuits, calculate the current flowing in the wire W3:

