Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the given parallelograms. Find the values of the unknowns x, y, z.
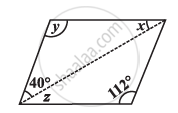
उत्तर
y = 112° (Opposite angles are equal)
x + y + 40° = 180° (Angle sum property of triangles)
x + 112° + 40° = 180°
x + 152° = 180°
x = 28°
z = x = 28° (Alternate interior angles)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider the given parallelograms. Find the values of the unknowns x, y, z.
In parallelogram ABCD, ∠A = 3 times ∠B. Find all the angles of the parallelogram. In the same parallelogram, if AB = 5x – 7 and CD = 3x +1 ; find the length of CD.
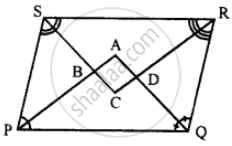
Given: Parallelogram ABCD in which diagonals AC and BD intersect at M.
Prove: M is the mid-point of LN.
In the following diagram, the bisectors of interior angles of the parallelogram PQRS enclose a quadrilateral ABCD.
Show that:
(i) ∠PSB + ∠SPB = 90°
(ii) ∠PBS = 90°
(iii) ∠ABC = 90°
(iv) ∠ADC = 90°
(v) ∠A = 90°
(vi) ABCD is a rectangle
Thus, the bisectors of the angles of a parallelogram enclose a rectangle.
If a triangle and a parallelogram lie on the same base and between the same parallels, then prove that the area of the triangle is equal to half of the area of parallelogram
The angle between the two altitudes of a parallelogram through the same vertex of an obtuse angle of the parallelogram is 30°. The measure of the obtuse angle is ______.
A diagonal of a parallelogram bisects an angle. Will it also bisect the other angle? Give reason.
In parallelogram ABCD, the angle bisector of ∠A bisects BC. Will angle bisector of B also bisect AD? Give reason.
Construct a parallelogram HOME with HO = 6 cm, HE = 4 cm and OE = 3 cm.
Draw a rough figure of a quadrilateral that is not a parallelogram but has exactly two opposite angles of equal measure.
