Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define refraction and state the laws of refraction.
उत्तर
The phenomenon of change in the direction of propagation of light when it passes obliquely from one transparent medium to another is called refraction of light.
Laws of refraction:-
- The incident ray and the refracted ray are on the opposite sides of the normal at the point of incidence, and all three lie in the same plane.
- For a given pair of media, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant.
`sin i/sin r=mu`
This constant is called the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first medium.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain how spectrum is formed.
When rays of light are incident on a glass slab then the incident ray and emergent ray are _________ each other.
- perpendicular
- parallel
- opposite
- concurrent
Write a short note on dispersion of light.
A student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab and marks the angle of incidence i, angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e, as shown.
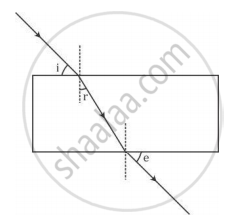
The correctly marked angle(s) is/are
(A) ∠ i only
(B) ∠ e only
(C) ∠ r only
(D) ∠ i and ∠ e
Four students P, Q, R and S traced the path of a ray of light passing through a glass slab for an angle of incidence 40° and measured the angle of refraction. The values as measured them were 18°; 22°; 25° and 30° respectively. The student who has performed the experiment methodically is
(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
A ray of light passes from water to air. How does the speed of light change?
Name a prism required for obtaining a spectrum of Ultraviolet light.
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why?
Which of the above wavelengths has a higher frequency?
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism change with increase in the angle of incidence. Draw a curve showing the variation in the angle of deviation with the angle of incidence at a prism surface.
How does the angle of minimum deviation produces by a prism change with increase in :
the refracting angle of prism?
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from air to a liquid.
- Write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
- Use Snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.

An object is viewed through a glass prism with its vertex pointing upwards. It appears to be displaced upward. Explain the reason.
A total reflecting right angled isosceles prism can be used to deviate a ray of light through:
(a) 30° (b) 60° (c) 75° (d) 90°.
Select from the following the best set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab:
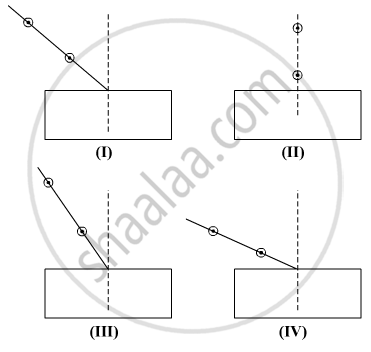
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
While tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab a student tabulated his observations as given below:
|
S.NO. |
∠i |
∠r |
∠e |
|
I |
60° |
40° |
61° |
|
II |
50° |
36° |
51° |
|
III |
40° |
28° |
39° |
|
IV |
30° |
20° |
31° |
The correct observations is:
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
While performing the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab, in which of the following experimental set-ups is a student likely to get best results? P1 and P2 are the positions of pins fixed by him.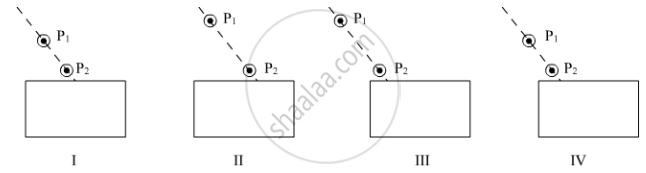
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Rahim recorded the following sets of observations while tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence.
|
S. No. |
Angle of incidence |
Angle of refraction |
Angle of emergence |
|
I |
45° |
41° |
45° |
|
II |
40° |
38° |
38° |
|
III |
45° |
41° |
40° |
|
IV |
41° |
45° |
41° |
The correct observation is recorded at serial number:
(1) I
(2) II
(3) III
(4) IV
Observe the figure and write accurate conclusion regarding refraction of light.
What is the correct reason for blinking / flickering of stars? Explain it.
a) The blasts in the stars.
b) Absorption of star light by the atmosphere.
c) Motion of the stars.
d) Changing refractive index of gases in the atmosphere.
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) What is the line XX' called?
(iii) Complete the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray either meets XX' at a point or appears to come from a point on XX'. Label it as F, What is this point called?
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
How does the deviation produced by a prism depend on the refraction index of its material.
Does the depth of a tank of water appear to change or remain the same when viewed normally from above?
A fish swimming in a pond seems nearer than it really is. Explain.
Express the refractive index μ of a medium in terms of the velocity of light.
After a robbery, if a window has been broken, there will be tiny particles of glass. Some of these will be found at the scene of the crime and some may be caught in the thief’s clothing. If the police can prove that these particles are identical, they have a strong case.
A method of doing this is to suspend the particles of glass in a special liquid. Light of a single colour is thrown through the liquid and the particles viewed through a microscope. The temperature of the liquid is then slowly altered. This alters the speed of light through the liquid (i.e., it alters the refractive index). At one particular temperature, the particles of glass disappear. It this happens at the same temperature for both sets of glass particles, they probably came from the same broken pane of glass.
Complete and copy the diagram to show how light bends when it travels from the liquid to the glass and back to the liquid, If the light slows down in the glass.
Draw a diagram to show the refraction of a monochromatic light ray through an equilateral prism. On the diagram, label the incident, refracted, and emergent rays. It also indicates the angle of deviation by the letter δ.
How does the angle of deviation produced by a prism depend on the angle of incidence of light at the prism surface? Draw a graph to illustrate your answer.
How will you verify the laws of refraction or how the refractive index of glass is determined in the laboratory?
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from air to glass. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
The velocity of light in diamond is 121000 kms-1. What is its refractive index?
Write the approximate values of speed of light in (i) air and (ii) glass. Use these values to calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to air.
