Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the correct reason for blinking / flickering of stars? Explain it.
a) The blasts in the stars.
b) Absorption of star light by the atmosphere.
c) Motion of the stars.
d) Changing refractive index of gases in the atmosphere.
उत्तर
d) Changing refractive index of gases in the atmosphere.
Atmosphere is unstable due to changing density and temperature of air, hence refractive index of air keeps changing continuously. The position and brightness of the star keep changing continuously and the star appears to be twinkling.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define refraction and state the laws of refraction.
Explain how the formation of a rainbow occurs.
Four students P, Q, R and S traced the path of a ray of light passing through a glass slab for an angle of incidence 40° and measured the angle of refraction. The values as measured them were 18°; 22°; 25° and 30° respectively. The student who has performed the experiment methodically is
(A) P
(B) Q
(C) R
(D) S
Write a relationship between the angle of incidence and angle of refractions for a given pair of media
Name one factor that affects the lateral displacement of light as it passes through a rectangular glass slab.
Draw the diagram of refraction of light in the glass slab
Observe the following figure and answer the questions given under it:
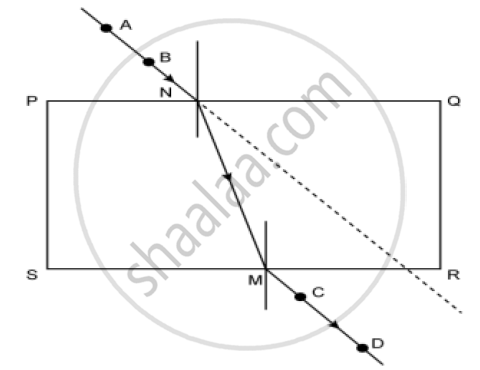
1) How many times does refraction take place in the above figure?
2) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from air to glass?
3) What happens to the ray of light when it passes from glass to air?
4) What are the rays AB and CD in the figure called?
5) Define refraction.
How must light travel out of a substance if it is not going to be refracted?
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
When a ray of light from air enters a denser medium, it ______.
The highest refractive index is of ______.
What do you understand by the statement the refractive index of glass is 1.5 for white light?
How is the angle of emergence related to the angle of incidence when prism is in the position of minimum deviation? Illustrate your answer with help of a labelled diagram using an equilateral prism?
The refractive index of glass is 1.5. From a point P inside a glass block, draw rays PA, PB and PC incident on the glass air surface at an angle of incidence 30°, 42° and 60° respectively.
- In the diagram show the approximate direction of these rays as they emerge out of the block.
- What is the angle of refraction for the ray PB?
`("Take" sin 42° =2/3)`
A ray of light enters a glass slab ABDC as shown in figure and strikes at the centre O of the circular part AC of the slab. The critical angle of glass is 42°. Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out from the slab. Mark the angles in the diagram wherever necessary.

A student traces the path of a ray of white light through a rectangular glass slab and marks, the angles of incidence (∠i) , refraction (∠r) and emergence (∠e) as shown. Which angle or angles has he not marked correctly?
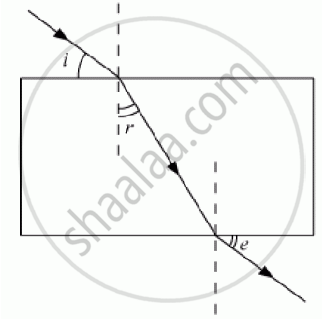
(A) ∠i only
(B) ∠i and ∠r
(C) ∠i and ∠e
(D) ∠r and ∠e
(i) What is the relation between the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` and the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
(ii) If the refractive index of water with respect to air `("_aμ_\text(w))` is`5/3`. Calculate the refractive index of air with respect to water `("_\text(w)μ_ a)` .
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
Define the term refractive index of a medium. What do you understand by the statement 'the refractive index of glass is 1.5 for white light'?
How does the deviation produced by a prism depend on the refraction index of its material.
A total reflecting equilateral prism can be used to deviate a ray of light through:
Name the phenomenon responsible in the following case:
Apparent bending of a stick in water
Name the phenomenon responsible in the following case:
Twinkling of stars
Why do the faces of persons sitting around campfire appear to shimmer?
Why upper surface of water contained in a beaker and above eye level appears silvery?
What is the refractive index of vacuum
Comment on the statement ‘The refractive index of glass is 3/2.’
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism?
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is defined: as gµa = sin i/sin r
If r = 90°, what is the corresponding angle i called?
After a robbery, if a window has been broken, there will be tiny particles of glass. Some of these will be found at the scene of the crime and some may be caught in the thief’s clothing. If the police can prove that these particles are identical, they have a strong case.
A method of doing this is to suspend the particles of glass in a special liquid. Light of a single colour is thrown through the liquid and the particles viewed through a microscope. The temperature of the liquid is then slowly altered. This alters the speed of light through the liquid (i.e., it alters the refractive index). At one particular temperature, the particles of glass disappear. It this happens at the same temperature for both sets of glass particles, they probably came from the same broken pane of glass.
Complete and copy the diagram to show how light bends when it travels from the liquid to the glass and back to the liquid, If the light slows down in the glass.
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from the air on a glass slab:
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the change in the path of the ray till it emerges from the glass slab.
(ii) Name the two rays that are parallel to each other.
(iii) Mark the lateral displacement in your diagram.
How will you verify the laws of refraction or how the refractive index of glass is determined in the laboratory?
Draw the ray diagram of a glass slab having medium A and B for the velocity of light ray VA and VB respectively and define Snell's law.
- If VB = 1.5 VA, then which medium is denser?
- What is the refractive index of A with respect to B?
- What is the refractive index of B with respect to A?
What is lateral displacement?
