Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive an expression for resistivity of a conductor in terms of the number density of charge carriers in the conductor and relaxation time.
उत्तर
The relationship between the relaxation time (τ) and drift velocity `(v_d)` is given by:
`v_d = -e((Eτ)/m)`
∴ `τ = ((v_d m))/e xx E`
Let L = Length of the conductor
A = Area of the conductor
n = free electron density
e = charge of the electron
E = Electric field
m = mass of the electron
τ = Relaxation time
The current flowing through the conductor is
I = `n eAv_d`
I = `n e A((eE)/m)τ`
Also, field E can be expressed as
E = `V/L`
The current flowing through the conductor is:
I = `(n e^2VAτ)/(mL)`
or `V/I = (mL)/(n e^2τA)`
or `R = (mL)/(n e^2τA)` ...`("from Ohm's law" V/I = R)`
or `R = m/(n e^2τ)(L/A)`
Electrical resistivity, `rho = m/(n e^2τ)` `...[∵ R = rho L/A]`
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the term drift velocity.
When a current is established in a wire, the free electrons drift in the direction opposite to the current. Does the number of free electrons in the wire continuously decrease?
Electrons are emitted by a hot filament and are accelerated by an electric field, as shown in the figure. The two stops at the left ensure that the electron beam has a uniform cross-section.
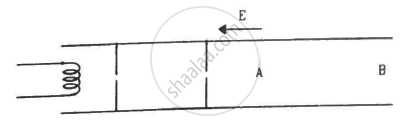
When a current I is set up in a wire of radius r, the drift velocity is vd· If the same current is set up through a wire of radius 2 r, the drift velocity will be:
An electric bulb.is rated 220 v and 100 watt power consumed by it when operated on 'no volt is:-
Is the momentum conserved when charge crosses a junction in an electric circuit? Why or why not?
- Consider circuit in figure. How much energy is absorbed by electrons from the initial state of no current (ignore thermal motion) to the state of drift velocity?
- Electrons give up energy at the rate of RI2 per second to the thermal energy. What time scale would one associate with energy in problem (a)? n = no of electron/volume = 1029/m3, length of circuit = 10 cm, cross-section = A = (1mm)2
Define relaxation time.
Consider two conducting wires A and B of the same diameter but made of different materials joined in series across a battery. The number density of electrons in A is 1.5 times that in B. Find the ratio of the drift velocity of electrons in wire A to that in wire B.
A potential difference (V) is applied across a conductor of length 'L' and cross-sectional area 'A'.
How will the drift velocity of electrons and the current density be affected if another identical conductor of the same material were connected in series with the first conductor? Justify your answers.
