Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Point in a plane equidistant from a given line.
उत्तर
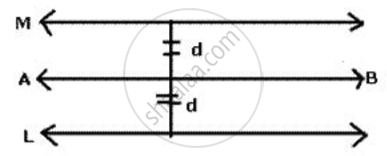
The locus of all points in a plane equidistant from a fixed line is represented by two parallel lines either side of it at a distanced away.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Describe the locus of a point in space, which is always at a distance of 4 cm from a fixed point.
Construct a triangle ABC, with AB = 5.6 cm, AC = BC = 9.2 cm. Find the points equidistant from AB and AC; and also 2 cm from BC. Measure the distance between the two points obtained.
Plot the points A(2, 9), B(–1, 3) and C(6, 3) on graph paper. On the same graph paper draw the locus of point A so that the area of ΔABC remains the same as A moves.
Draw and describe the lorus in the following cases:
The lorus of a point in rhombus ABCD which is equidistant from AB and AD .
Describe completely the locus of point in the following cases:
Midpoint of radii of a circle.
Describe completely the locus of point in the following cases:
Centre of a ball, rolling along a straight line on a level floor.
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Centre of a circle of varying radius and touching the two arms of ∠ ABC.
Draw and describe the locus in the following cases :
The locus of a point in the rhombus ABCD which is equidistant from the point A and C
Construct a triangle BPC given BC = 5 cm, BP = 4 cm and .
i) complete the rectangle ABCD such that:
a) P is equidistant from AB and BCV
b) P is equidistant from C and D.
ii) Measure and record the length of AB.
Use ruler and compasses only for the following questions:
Construct triangle BCP, when CB = 5 cm, BP = 4 cm, ∠PBC = 45°.
Complete the rectangle ABCD such that :
(i) P is equidistant from AB and BC and
(ii) P is equidistant from C and D. Measure and write down the length of AB.
