Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Point in a plane equidistant from a given line.
उत्तर
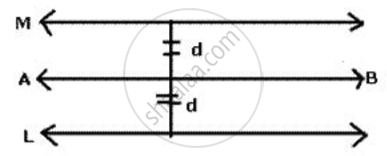
The locus of all points in a plane equidistant from a fixed line is represented by two parallel lines either side of it at a distanced away.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Describe the locus of a point P, so that:
AB2 = AP2 + BP2,
where A and B are two fixed points.
State the locus of a point in a rhombus ABCD, which is equidistant
- from AB and AD;
- from the vertices A and C.
Construct an isosceles triangle ABC such that AB = 6 cm, BC = AC = 4 cm. Bisect ∠C internally and mark a point P on this bisector such that CP = 5 cm. Find the points Q and R which are 5 cm from P and also 5 cm from the line AB.
Without using set squares or protractor, construct a quadrilateral ABCD in which ∠ BAD = 45° , AD = AB = 6 cm, BC= 3.6 cm and CD=5 cm. Locate the point P on BD which is equidistant from BC and CD.
A and B are fixed points while Pis a moving point, moving in a way that it is always equidistant from A and B. What is the locus of the path traced out by the pcint P?
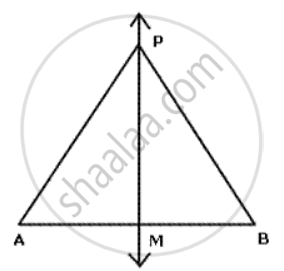
In given figure 1 ABCD is an arrowhead. AB = AD and BC = CD. Prove th at AC produced bisects BD at right angles at the point M

Draw and describe the lorus in the following cases:
The Iocus of the mid-points of all parallel chords of a circle.
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Centre of a circle of varying radius and touching the two arms of ∠ ABC.
Use ruler and compass only for the following question. All construction lines and arcs must be clearly shown.
- Construct a ΔABC in which BC = 6.5 cm, ∠ABC = 60°, AB = 5 cm.
- Construct the locus of points at a distance of 3.5 cm from A.
- Construct the locus of points equidistant from AC and BC.
- Mark 2 points X and Y which are at a distance of 3.5 cm from A and also equidistant from AC and BC. Measure XY.
State and draw the locus of a point equidistant from two given parallel lines.
