Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe completely the locus of point in the following cases:
Centre of a ball, rolling along a straight line on a level floor.
उत्तर
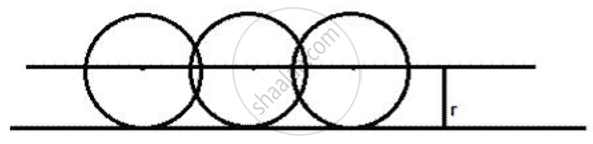
The locus of the centre of a ball, rolling along a straight line on a level floor will be a straight Iine paralIel to the floor at a di stance equal to the radius of the ball.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Angle ABC = 60° and BA = BC = 8 cm. The mid-points of BA and BC are M and N respectively. Draw and describe the locus of a point which is:
- equidistant from BA and BC.
- 4 cm from M.
- 4 cm from N.
Mark the point P, which is 4 cm from both M and N, and equidistant from BA and BC. Join MP and NP, and describe the figure BMPN.
Draw an angle ABC = 75°. Find a point P such that P is at a distance of 2 cm from AB and 1.5 cm from BC.
Construct a rhombus ABCD whose diagonals AC and BD are 8 cm and 6 cm respectively. Find by construction a point P equidistant from AB and AD and also from C and D.
Construct a ti.PQR, in which PQ=S. 5 cm, QR=3. 2 cm and PR=4.8 cm. Draw the locus of a point which moves so that it is always 2.5 cm from Q.
A and B are fixed points while Pis a moving point, moving in a way that it is always equidistant from A and B. What is the locus of the path traced out by the pcint P?
Describe completely the locus of point in the following cases:
Midpoint of radii of a circle.
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Point in a plane equidistant from a given line.
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Centre of a circle of varying radius and touching the two arms of ∠ ABC.
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Centre of a cirde of radius 2 cm and touching a fixed circle of radius 3 cm with centre O.
Using a ruler and compass only:
(i) Construct a triangle ABC with BC = 6 cm, ∠ABC = 120° and AB = 3.5 cm.
(ii) In the above figure, draw a circle with BC as diameter. Find a point 'P' on the circumference of the circle which is equidistant from Ab and BC.
Measure ∠BCP.
