Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the construction of photoelectric cell.
उत्तर १
A photoelectric cell is device which converts light energy into electrical energy. It works on the principle of photoelectric effect.
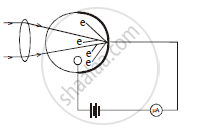
Construction : A photoelectric cell consist a small evacuated bulb. A thin layer of an alkali metal is deposited on inner surface of the bulb. The bulb is made of quartz, if cell is used with ultraviolet light. If the cell is to be used with visible light only. the bulb is made of ordinary glass. A small portion of the surface of bulb is left uncoated and serves as a window for incoming light. The coated surface of the bulb acts as cathode. The anode is in shape of sphere.
उत्तर २
Construction —
- Photocell consists of evacuated glass tube containing two electrodes emitter (K) and collector (A).
- The emitter is shaped in the form of a semi hollow cylinder. It is always kept at a negative potential.
- The collector is in the form of a matal rod and fixed at the axis of the semi-cylinderical emitter. The collector is always kept as a positive potential.
- The glass tube is fitted on non-metallic base and pins are provided at the base for external connection.
Working —
- The emitter is connected to negative terminal and collector is connected to positive terminal of a battery.
- A radiation of frequency more than threshold frequency of material of emitter is made incident on the emitter. Photo-emissions take place. The photoelectrons are attracted towards the collector which is positive w.r.t the emitter. Thus, current flows in the circuit.
- If the intensity of incident radiation is increased, the photoelectric current increases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A proton and an α-particle have the same de-Broglie wavelength Determine the ratio of their speeds.
Calculate the momentum of the electrons accelerated through a potential difference of 56 V.
An electron and a photon each have a wavelength of 1.00 nm. Find
(a) their momenta,
(b) the energy of the photon, and
(c) the kinetic energy of electron.
For what kinetic energy of a neutron will the associated de Broglie wavelength be 1.40 × 10−10 m?
What is the de Broglie wavelength of a nitrogen molecule in air at 300 K? Assume that the molecule is moving with the root-mean square speed of molecules at this temperature. (Atomic mass of nitrogen = 14.0076 u)
Compute the typical de Broglie wavelength of an electron in a metal at 27°C and compare it with the mean separation between two electrons in a metal which is given to be about 2 × 10−10 m.
State any one phenomenon in which moving particles exhibit wave nature.
Why photoelectric effect cannot be explained on the basis of wave nature of light? Give reasons.
When a light wave travels from air to glass
What are matter waves?
Which one of the following deflect in electric field
A proton and α-particle are accelerated through the same potential difference. The ratio of the de-Broglie wavelength λp to that λα is _______.
An electromagnetic wave of wavelength ‘λ’ is incident on a photosensitive surface of negligible work function. If ‘m’ mass is of photoelectron emitted from the surface has de-Broglie wavelength λd, then ______
A proton, a neutron, an electron and an α-particle have same energy. Then their de Broglie wavelengths compare as ______.
An electron is moving with an initial velocity `v = v_0hati` and is in a magnetic field `B = B_0hatj`. Then it’s de Broglie wavelength ______.
Two particles A1 sand A2 of masses m1, m2 (m1 > m2) have the same de Broglie wavelength. Then ______.
- their momenta are the same.
- their energies are the same.
- energy of A1 is less than the energy of A2.
- energy of A1 is more than the energy of A2.
The de Broglie wavelength of a photon is twice the de Broglie wavelength of an electron. The speed of the electron is `v_e = c/100`. Then ______.
- `E_e/E_p = 10^-4`
- `E_e/E_p = 10^-2`
- `p_e/(m_ec) = 10^-2`
- `p_e/(m_ec) = 10^-4`
A particle moves in a closed orbit around the origin, due to a force which is directed towards the origin. The de Broglie wavelength of the particle varies cyclically between two values λ1, λ2 with λ1 > λ2. Which of the following statement are true?
- The particle could be moving in a circular orbit with origin as centre.
- The particle could be moving in an elliptic orbit with origin as its focus.
- When the de Broglie wavelength is λ1, the particle is nearer the origin than when its value is λ2.
- When the de Broglie wavelength is λ2, the particle is nearer the origin than when its value is λ1.
A particle A with a mass m A is moving with a velocity v and hits a particle B (mass mB) at rest (one dimensional motion). Find the change in the de Broglie wavelength of the particle A. Treat the collision as elastic.
An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 100 V. Calculate:
- The speed acquired by the alpha particle, and
- The de-Broglie wavelength is associated with it.
(Take mass of alpha particle = 6.4 × 10−27 kg)
Given below are two statements:
Statement - I: Two photons having equal linear momenta have equal wavelengths.
Statement - II: If the wavelength of photon is decreased, then the momentum and energy of a photon will also decrease.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
How will the de-Broglie wavelength associated with an electron be affected when the velocity of the electron decreases? Justify your answer.
E, c and `v` represent the energy, velocity and frequency of a photon. Which of the following represents its wavelength?
Matter waves are ______.
