Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a labelled diagram to show how iron is electroplated with copper.
उत्तर
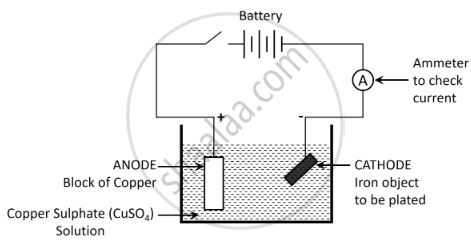
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the metallic ions that should be present in the electrolyte when an article made of copper is to be electroplated with silver.
State one relevant observation for the following:
At the anode when aqueous copper sulphate solution is electrolysed using copper electrodes.
State the electrode reaction at the anode during electrolysis of:
Aqueous copper sulphate solution.
Give reason for the following:
For electroplating with silver, silver nitrate is not used as an electrolyte.
List out the main applications of electrolysis.
The following question relate to the electroplating of an article with silver.
Name the electrode formed by the article which is to be plated.
The following questions are about electroplating of copper wire with silver.
(a) What ions must be present in the electrolyte?
(b) Of what substance must the anode be made up of?
(c) What will the cathode be made up of?
(d) Write the equation for the reaction which takes place at the cathode.
Which solution is preferred as electrolyte, CuSO4 or FeSO4?
Describe what happens to the iron object and the copper rod.
Electroplating steel objects with silver involves a three-step process.
Step 1: A coating of copper is applied to the object.
Step 2: A coating of nickel is applied to the object.
Step 3: The coating of silver is applied to the object.
-
- A diagram of the apparatus used for step 1 is shown
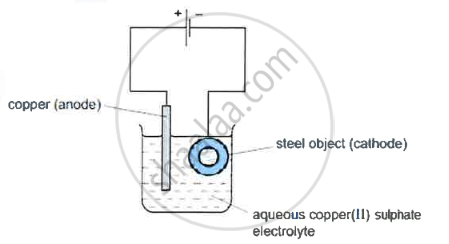
- The chemical process taking place on the surface of the object is \[\ce{Cu^2+(aq) + 2e- ->Cu(s)}\]
What is the observation seen on the surface of the object? - Explain why the concentration of copper ions in the electrolyte remains constant throughout step 1.
- The chemical process taking place on the surface of the object is \[\ce{Cu^2+(aq) + 2e- ->Cu(s)}\]
- A diagram of the apparatus used for step 1 is shown
- Give two changes which would be needed in order to coat nickel on to the object in step 2.
- Write down the reaction taking place at the positive electrode during step 3.
