Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe what happens to the iron object and the copper rod.
उत्तर
The copper anode continuously dissolves as ions in solution and is replaced periodically. The electrolyte dissociates into Cu2+ ions, which migrate towards the iron object taken as the cathode and are deposited as neutral copper atoms on the cathode.
Electrolyte: Aqueous solution of nickel sulphate
Dissociation: \[\ce{CuSO4 ⇌ Cu^2^+ + SO^2^-4}\]
\[\ce{H2O ⇌ H^+ + OH^-}\]
Electrodes:
- Cathode: Article to be electroplated
- Anode: Block of pure copper
Electrode reactions:
- Reaction at cathode: \[\ce{Cu^{2+} + 2e^- -> Cu}\] (deposited)
- Reaction at anode: \[\ce{Cu - 2e^- -> Cu^{2+}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the metallic ions that should be present in the electrolyte when an article made of copper is to be electroplated with silver.
State one relevant observation for the following:
At the anode when aqueous copper sulphate solution is electrolysed using copper electrodes.
Give one word or phrase for the following:
Electrolytic deposition of a superior metal on a baser metal.
How would you change Cu2+ ion to Cu?
An electrolytic cell is set up using two platinum electrodes and an aqueous solution of copper (II) sulphate,
(a)draw a labelled diagram of the electrolytic cell,
(b)Name the ions present in the cell,
(c)Name the ions migrating towards the anode,
(d)Name the ions migrating towards the cathode,
(e)Name the ions which will not be discharged at electrodes during electrolysis,
(f)Write the reaction at the cathode,
(g)Write the reaction at the anode,
(h)Name the spectator ion in the solution.
Give reason for the following:
The blue colour of aqueous copper sulphate fades when it is electrolysed using platinum electrodes.
Give reason for the following:
For electroplating with silver, silver nitrate is not used as an electrolyte.
Give three applications of electrolysis.
Draw a labelled diagram to show how iron is electroplated with copper.
Electroplating steel objects with silver involves a three-step process.
Step 1: A coating of copper is applied to the object.
Step 2: A coating of nickel is applied to the object.
Step 3: The coating of silver is applied to the object.
-
- A diagram of the apparatus used for step 1 is shown
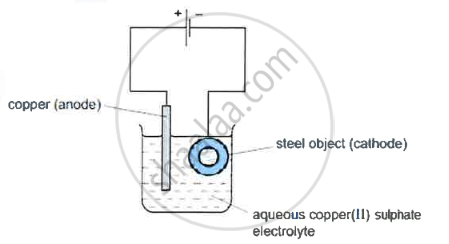
- The chemical process taking place on the surface of the object is \[\ce{Cu^2+(aq) + 2e- ->Cu(s)}\]
What is the observation seen on the surface of the object? - Explain why the concentration of copper ions in the electrolyte remains constant throughout step 1.
- The chemical process taking place on the surface of the object is \[\ce{Cu^2+(aq) + 2e- ->Cu(s)}\]
- A diagram of the apparatus used for step 1 is shown
- Give two changes which would be needed in order to coat nickel on to the object in step 2.
- Write down the reaction taking place at the positive electrode during step 3.
