Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw equipotential surfaces corresponding to a uniform electric field in the z-directions.
उत्तर
For constant electric field vector E
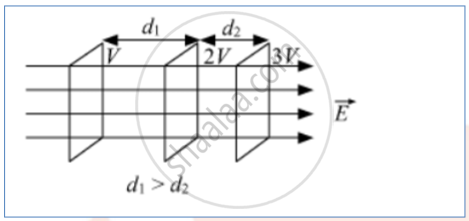
For increasing electric field
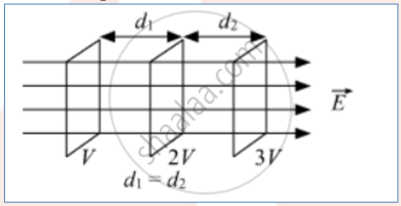
Difference:
For constant electric field, the equipotential surfaces are equidistant for the same potential difference between these surfaces; while for increasing electric field, the separation between these surfaces decreases, in the direction of the increasing field, for the same potential difference between them.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) If two similar large plates, each of area A having surface charge densities +σ and –σ are separated by a distance d in air, find the expressions for
(a) field at points between the two plates and on outer side of the plates. Specify the direction of the field in each case.
(b) the potential difference between the plates.
(c) the capacitance of the capacitor so formed.
(ii) Two metallic spheres of Radii R and 2R are charged so that both of these have same surface charge density σ. If they are connected to each other with a conducting wire, inn which direction will the charge flow and why?
Two identical circular loops 1 and 2 of radius R each have linear charge densities −λ and +λ C/m respectively. The loops are placed coaxially with their centres `Rsqrt3` distance apart. Find the magnitude and direction of the net electric field at the centre of loop 1.
Plot a graph showing the variation of resistivity of a conductor with temperature.
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
The electric field in a region is given by
`vec"E"= 3/5"E"_0 vec"i" + 4/5 "E"_0 vec "i" "with" " E"_0 = 2.0 xx 10^3 "N""C"^-1.`
Find the flux of this field through a rectangular surface of area 0⋅2 m2 parallel to the y-z plane.
A long cylindrical wire carries a positive charge of linear density 2.0 × 10-8 C m -1 An electron revolves around it in a circular path under the influence of the attractive electrostatic force. Find the kinetic energy of the electron. Note that it is independent of the radius.
One end of a 10 cm long silk thread is fixed to a large vertical surface of a charged non-conducting plate and the other end is fastened to a small ball of mass 10 g and a charge of 4.0× 10-6 C. In equilibrium, the thread makes an angle of 60° with the vertical (a) Find the tension in the string in equilibrium. (b) Suppose the ball is slightly pushed aside and released. Find the time period of the small oscillations.
Some equipotential surface is shown in the figure. What can you say about the magnitude and the direction of the electric field?
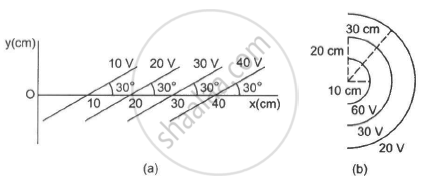
Answer the following question.
Prove that the average energy density of the oscillating electric field is equal to that of the oscillating magnetic field.
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
