Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
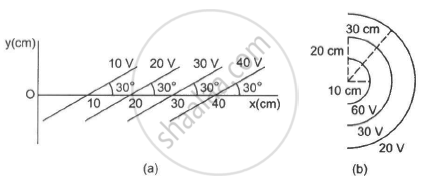
Some equipotential surface is shown in the figure. What can you say about the magnitude and the direction of the electric field?
उत्तर
(a) The electric field is always perpendicular to the equipotential surface. (As shown in the figure)
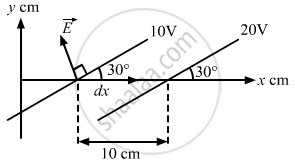
So, the angle between \[\vec{E} \text{ and } \vec{dx}\] = \[90^\circ+ 30^\circ\]
Change in potential in the first and second equipotential surfaces, dV = 10 V
so,
\[ \Rightarrow E(10 \times {10}^{- 2} )\cos120^\circ= - 10\]
\[ \Rightarrow E = 200\] V/m
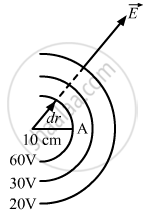
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{q}{4\pi \epsilon_0} = 0 . 6\]
The electric field is radially outward, decreasing with increasing distance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a large plastic plate. The electric field at a point P close to the centre of the plate is 10 V m−1. If the plastic plate is replaced by a copper plate of the same geometrical dimensions and carrying the same charge Q, the electric field at the point P will become
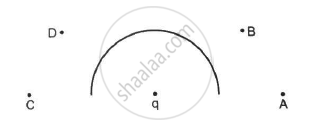
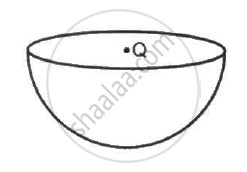
In the following figure shows a charge q placed at the centre of a hemisphere. A second charge Q is placed at one of the positions A, B, C and D. In which position(s) of this second charge, the flux of the electric field through the hemisphere remains unchanged?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
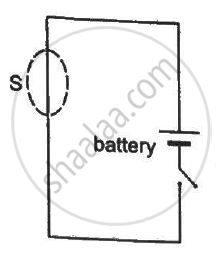
A closed surface S is constructed around a conducting wire connected to a battery and a switch in the following figure. As the switch is closed, the free electrons in the wire start moving along the wire. In any time interval, the number of electrons entering the closed surface S is equal to the number of electrons leaving it. On closing the switch, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface
(a) is increased
(b) is decreased
(c) remains unchanged
(d) remains zero
A charge Q is placed at the centre of an imaginary hemispherical surface. Using symmetry arguments and Gauss's Law, find the flux of the electric field due to this charge through the surface of the hemisphere in the following figure.
The radius of a gold nucleus (Z = 79) is about 7.0 × 10-10 m. Assume that the positive charge is distributed uniformly throughout the nuclear volume. Find the strength of the electric field at (a) the surface of the nucleus and (b) at the middle point of a radius. Remembering that gold is a conductor, is it justified to assume that the positive charge is uniformly distributed over the entire volume of the nucleus and does not come to the outer surface?
A charge Q is placed at the centre of an uncharged, hollow metallic sphere of radius a. (a) Find the surface. (b) If a charge q is put on the sphere, what would be the surface charge densities on the inner and outer surfaces? (c) Find the electric field inside the sphere at a distance x from the centre in the situations (a) and (b).
Consider the following very rough model of a beryllium atom. The nucleus has four protons and four neutrons confined to a small volume of radius 10−15 m. The two 1 selectrons make a spherical charge cloud at an average distance of 1⋅3 ×10−11 m from the nucleus, whereas the two 2 s electrons make another spherical cloud at an average distance of 5⋅2 × 10−11 m from the nucleus. Find three electric fields at (a) a point just inside the 1 s cloud and (b) a point just inside the 2 s cloud.
A non-conducting sheet of large surface area and thickness d contains a uniform charge distribution of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the plate, at a distance x from the central plane. Draw a qualitative graph of E against x for 0 < x < d.
A charged particle with a charge of −2⋅0 × 10−6 C is placed close to a non-conducting plate with a surface charge density of 4.0 × 10-6Cm0-2. Find the force of attraction between the particle and the plate.
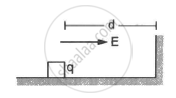
A block of mass containing a net positive charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table which terminates in a vertical wall as shown in the figure. The distance of the block from the wall is d. A horizontal electric field E towards the right is switched on. Assuming elastic collisions (if any), find the time period of the resulting oscillatory motion. Is it a simple harmonic motion?
Consider a circular ring of radius r, uniformly charged with linear charge density λ. Find the electric potential at a point on the axis at a distance x from the centre of the ring. Using this expression for the potential, find the electric field at this point.
A uniform field of 2.0 NC−1 exists in space in the x-direction. (a) Taking the potential at the origin to be zero, write an expression for the potential at a general point (x, y, z). (b) At which point, the potential is 25 V? (c) If the potential at the origin is taken to be 100 V, what will be the expression for the potential at a general point? (d) What will be the potential at the origin if the potential at infinity is taken to be zero? Is it practical to choose the potential at infinity to be zero?
Electric field at a point is defined as ______.
When a comb rubbed with dry hair attracts pieces of paper. This is because the ______.
The force per unit charge is known as ______.
