Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a large plastic plate. The electric field at a point P close to the centre of the plate is 10 V m−1. If the plastic plate is replaced by a copper plate of the same geometrical dimensions and carrying the same charge Q, the electric field at the point P will become
विकल्प
zero
5 V m−1
10 V m−1
20 V m−1
उत्तर
10 V m-1
The electric field remains same for the plastic plate and the copper plate, as both are considered to be infinite plane sheets. So, it does not matter whether the plate is conducting or non-conducting.
The electric field due to both the plates,
`"E" = σ /ε_0`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
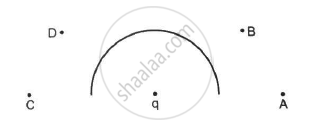
In the following figure shows a charge q placed at the centre of a hemisphere. A second charge Q is placed at one of the positions A, B, C and D. In which position(s) of this second charge, the flux of the electric field through the hemisphere remains unchanged?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
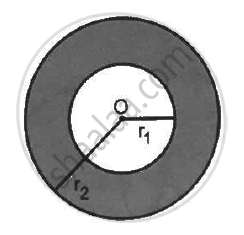
A charge Q is distributed uniformly within the material of a hollow sphere of inner and outer radii r1 and r2 (see the figure). Find the electric field at a point P at a distance x away from the centre for r1 < x < r. Draw a rough graph showing the electric field as a function of x for 0 < x < 2r2 (see the figure).
Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4 cm away from a line charge of density 2 × 10-6 Cm-1.
A long cylindrical wire carries a positive charge of linear density 2.0 × 10-8 C m -1 An electron revolves around it in a circular path under the influence of the attractive electrostatic force. Find the kinetic energy of the electron. Note that it is independent of the radius.
A non-conducting sheet of large surface area and thickness d contains a uniform charge distribution of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the plate, at a distance x from the central plane. Draw a qualitative graph of E against x for 0 < x < d.
A charged particle with a charge of −2⋅0 × 10−6 C is placed close to a non-conducting plate with a surface charge density of 4.0 × 10-6Cm0-2. Find the force of attraction between the particle and the plate.
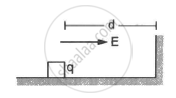
A block of mass containing a net positive charge q is placed on a smooth horizontal table which terminates in a vertical wall as shown in the figure. The distance of the block from the wall is d. A horizontal electric field E towards the right is switched on. Assuming elastic collisions (if any), find the time period of the resulting oscillatory motion. Is it a simple harmonic motion?
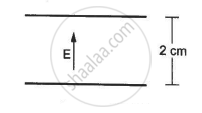
An electric field of magnitude 1000 NC−1 is produced between two parallel plates with a separation of 2.0 cm, as shown in the figure. (a) What is the potential difference between the plates? (b) With what minimum speed should an electron be projected from the lower place in the direction of the field, so that it may reach the upper plate? (c) Suppose the electron is projected from the lower place with the speed calculated in part (b). The direction of projection makes an angle of 60° with the field. Find the maximum height reached by the electron.
A uniform field of 2.0 NC−1 exists in space in the x-direction. (a) Taking the potential at the origin to be zero, write an expression for the potential at a general point (x, y, z). (b) At which point, the potential is 25 V? (c) If the potential at the origin is taken to be 100 V, what will be the expression for the potential at a general point? (d) What will be the potential at the origin if the potential at infinity is taken to be zero? Is it practical to choose the potential at infinity to be zero?
Draw equipotential surfaces corresponding to a uniform electric field in the z-directions.
Answer the following question.
Prove that the average energy density of the oscillating electric field is equal to that of the oscillating magnetic field.
Electric field at a point is defined as ______.
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
