Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A metallic particle with no net charge is placed near a finite metal plate carrying a positive charge. The electric force on the particle will be
विकल्प
towards the plate
away from the plate
parallel to the plate
zero
उत्तर
towards the plate
The particle is a conductor. When it is brought near a positively charged metal plate, opposite charge is induced on its face nearer to the plate, i.e. negative and the same amount of charge, but of opposite polarity, goes to the farther end, i.e. positive.
Now, the attractive force is due to charges of opposite polarity. As they are at a lesser distance than the same polarity charges, the force of attraction is greater than the force of repulsion. In other words, the force on the particle is towards the plate.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
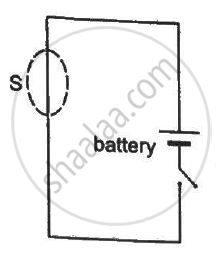
A closed surface S is constructed around a conducting wire connected to a battery and a switch in the following figure. As the switch is closed, the free electrons in the wire start moving along the wire. In any time interval, the number of electrons entering the closed surface S is equal to the number of electrons leaving it. On closing the switch, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface
(a) is increased
(b) is decreased
(c) remains unchanged
(d) remains zero
A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a rod of length l. Consider a hypothetical cube of edge l with the centre of the cube at one end of the rod. Find the minimum possible flux of the electric field through the entire surface of the cube.
The electric field in a region is given by `vec"E" = ("E"_0 "x")/"l" vec"i".`
Find the charge contained inside the cubical volume bound by the surfaces
x =0, x =a, y=0, y=a, z=0 and z=a. Take
`"E"_0 = 5 xx 10^3 "N""C"^-1 , "l" =2 "cm" " and" " a" = 1 "cm" `
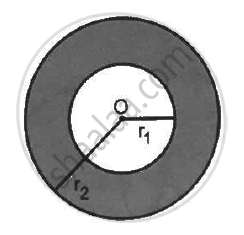
A charge Q is distributed uniformly within the material of a hollow sphere of inner and outer radii r1 and r2 (see the figure). Find the electric field at a point P at a distance x away from the centre for r1 < x < r. Draw a rough graph showing the electric field as a function of x for 0 < x < 2r2 (see the figure).
Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4 cm away from a line charge of density 2 × 10-6 Cm-1.
A long cylindrical wire carries a positive charge of linear density 2.0 × 10-8 C m -1 An electron revolves around it in a circular path under the influence of the attractive electrostatic force. Find the kinetic energy of the electron. Note that it is independent of the radius.
A non-conducting sheet of large surface area and thickness d contains a uniform charge distribution of density ρ. Find the electric field at a point P inside the plate, at a distance x from the central plane. Draw a qualitative graph of E against x for 0 < x < d.
A charged particle with a charge of −2⋅0 × 10−6 C is placed close to a non-conducting plate with a surface charge density of 4.0 × 10-6Cm0-2. Find the force of attraction between the particle and the plate.
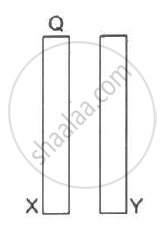
Two conducting plates X and Y, each with a large surface area A (on one side), are placed parallel to each other, as shown in the following figure . Plate X is given a charge Q,whereas the other is kept neutral. Find (a) the surface charge density at the inner surface of plate X (b) the electric field at a point to the left of the plates (c) the electric field at a point in between the plates and (d) the electric field at a point to the right of the plates.
A uniform electric field of 10 N C−1 exists in the vertically downward direction. Find the increase in the electric potential as one goes up through a height of 50 cm.
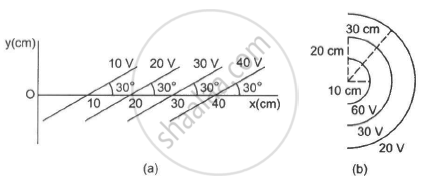
Some equipotential surface is shown in the figure. What can you say about the magnitude and the direction of the electric field?
A uniform field of 2.0 NC−1 exists in space in the x-direction. (a) Taking the potential at the origin to be zero, write an expression for the potential at a general point (x, y, z). (b) At which point, the potential is 25 V? (c) If the potential at the origin is taken to be 100 V, what will be the expression for the potential at a general point? (d) What will be the potential at the origin if the potential at infinity is taken to be zero? Is it practical to choose the potential at infinity to be zero?
Electric field at a point is defined as ______.
When a comb rubbed with dry hair attracts pieces of paper. This is because the ______.
Two charged conducting spheres of radii a and b are connected to each other by a wire. Find the ratio of the electric fields at their surfaces.
