Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain Hoffmann’s exhaustive alkylation with suitable reactions.
उत्तर
Hofmann’s exhaustive alkylation of amines:
- When a primary amine is heated with excess of primary alkyl halide it gives a mixture of secondary amine, tertiary amine along with tetraalkylammonium halide. This can be given as,
\[\ce{\underset{\text{1° Amine}}{R - NH2} ->[R - X][-HX] \underset{\text{2° Amine}}{R2NH} ->[R - X][-HX] \underset{\text{3° Amine}}{R3N} ->[R - X][-HX] \underset{\text{Tetraalkyl ammonium halide}}{R4N+X-}}\] - If the excess alkyl halide is used tetraalkylammonium halide is obtained as a major product and the reaction is known as exhaustive alkylation of amines.
- Tetraalkylammonium halides or quaternary ammonium salts are the derivatives of ammonium salts in which all the four hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen in N+H4 are replaced by four alkyl groups (same or different).
- Tetraalkylammonium halides are crystalline solids.
- Primary, secondary and tertiary amines consume three, two and one moles of alkyl halide respectively to get converted into quaternary ammonium salt.
- The reaction is carried out in presence of mild base NaHCO3, to neutralize the large quantity of HX formed.
- If the alkyl halide is methyl iodide, the reaction is called exhaustive methylation of amines.
e.g. When methylamine is heated with excess methyl iodide, it gives tetramethyl ammonium iodide.
\[\ce{\underset{\text{Methylamine}}{CH3 - NH2} + \underset{\text{Methyl iodide}}{CH3 - I} ->[\Delta] \underset{\text{Dimethylamine}}{(CH3)2NH} + HI}\]
\[\ce{(CH3)2 - NH + CH3 - I ->[\Delta] \underset{\text{Trimethyl amine}}{(CH3)3N} + HI}\]
\[\ce{(CH3)3N + CH3 - I ->[\Delta] \underset{\text{Tetramethyl ammonium iodide}}{(CH3)4N+I-}}\]
संबंधित प्रश्न
How do you convert the following: C6H5CONH2 to C6H5NH2
Write a short note on the following:
Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction
Accomplish the following conversions: Benzamide to toluene
Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reaction:
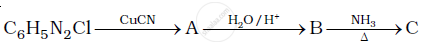
Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reaction:
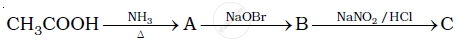
Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions :
Give the structures of A, B and C in the following reactions :

Answer in one sentence.
Predict the product of the following reaction.
\[\ce{Nitrobenzene ->[Sn/conc.HCl]?}\]
Answer the following
Identify A and B in the following reactions.
\[\ce{C6H5CH2Br->[alco.][KCN]A ->[Na/ethanol]B.}\]
Write reactions to prepare ethanamine from Acetonitrile.
The following amines is the product of Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
Mendius reaction is used to convert _____________
Write the order of reactivity of alkyl halides with ammonia.
Identify compound 'B' in following series of reactions?
\[\ce{Acetonitrile ->[Na/alcohol] A ->[NaNO2/dil.HCI] B}\]
Identify the product 'A' in the following reaction.
\[\ce{Aniline ->[(CH3CO)2O][Pyridine] A}\]
The end product C of the following reaction is
\[\ce{C2H5NH2 ->[HNO2] A ->[PCl5] B ->[NH3][Alcohol] C}\]
What product is formed when \[\ce{R - C ≡ N}\] is hydrolysed?
The reduction of alkyl cyanide with sodium and ethanol to give primary amines is, ____________.
In aqueous phase the order of basic strength of alkylamine is ______.
Which of the following amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
Which of the following compounds is obtained when quaternary ammonium hydroxide is strongly heated?
Which of the following does NOT give carbylamine test?
Which of the following reactions does NOT yield an amine?
Nitro compounds are reduced by iron scrap and hydrochloric acid to yield one of the following compounds:
Quaternary ammonium salt is formed:
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Alkyl halides are insoluble in water.
Reason (R): Alkyl halides have halogen attached to sp3 hybrid carbon.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
The best reagent for converting, 2-phenylpropanamide into 1- phenylethanamine is ______.
Which of the following compounds is the weakest Brönsted base?
Which of the following methods of preparation of amines will give same number of carbon atoms in the chain of amines as in the reactant?
What is the product when \[\ce{C6H5CH2NH2}\] reacts with \[\ce{HNO2}\]?
Suggest a route by which the following conversion can be accomplished.
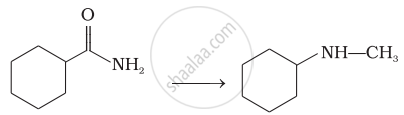
How will you carry out the following conversion?
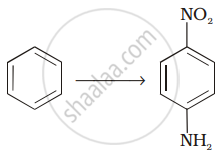
How will you carry out the following conversion?
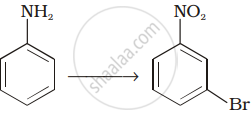
Match the reactions given in Column I with the statements given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Ammonolysis | (a) | Amine with lesser number of carbon atoms |
| (ii) | Gabriel phthalimide synthesis | (b) | Detection test for primary amines. |
| (iii) | Hoffmann Bromamide reaction | (c) | Reaction of phthalimide with \[\ce{KOH}\] and \[\ce{R-X}\] |
| (iv) | Carbylamine reaction | (d) | Reaction of alkylhalides with \[\ce{NH3}\] |
Account for the following:
Aniline cannot be prepared by the ammonolysis of chlorobenzene under normal conditions.
The Gabriels' phthalimide synthesis is used in the synthesis of
The compound X is which of the following?
\[\ce{CH3CN ->[Na + C2H5OH] x}\]
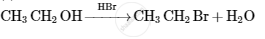
Ethylamine can be prepared by the action of bromine and caustic potash on which compound?
Acetamide and ethyl amide can be distinguished by reacting with.
C6H5CONHCH3 can be converted into C6H5CH2NHCH3 by:-
When primary amines are treated with HCl, the product obtained is which of the following?
Which of the following CANNOT be prepared by ammonolysis of alkyl halide?
A compound 'A' on reduction with iron scrap and hydrochloric acid gives compound 'B' with molecular formula C6H7N. Compound 'B' on reaction with CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH produces an obnoxious smell of carbylamine due to the formation of 'C'. Identify 'A', 'B' and 'C' and write the chemical reactions involved.
Give reasons for the following:
Ammonolysis of alkyl halides is not a good method to prepare pure primary amines.
Which of the following compound gives pink colour on reaction with phthalic anhydride in cone. H2SO4 followed by treatment with NaOH?
- Phenyl methenamine
- N, N - Dimethylaniline
- N - Methyl aniline
- Benzenamine
Choose the correct order of the basic nature of the above amines.
The amine 'A' when treated with nitrous acid gives yellow oily substance. The amine A is ______.
Amides can be converted into amines by the reaction named ______.
Write a short note on the following:
Ammonolysis.
Write short notes on the following:
Ammonolysis
