Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain in detail the idea of weightlessness using the lift as an example.
उत्तर
When a man is standing in the elevator, there are two forces acting on him.
1. Gravitational force which acts downward. If we take the vertical direction as a positive y-direction, the gravitational force acting on the man is `vec"F"_"G" = -"mg"hat"j"`
2. The normal force exerted by floor on the man which acts vertically upward, `vec"N" = "N"hat"j"`
The weightlessness of freely falling bodies: Freely falling objects experience only gravitational force. As they fall freely, they are not in contact with any surface (by neglecting air friction). The normal force acting on the object is zero. The downward acceleration is equal to the acceleration due to the gravity of the Earth, i.e., (a = g)
Newton’s second law acting on the man N = m(g – a)
a = g ∴ N = m(g – g) = 0.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The time period of a satellite orbiting Earth in a circular orbit is independent of
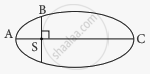
The kinetic energies of a planet in an elliptical orbit about the Sun, at positions A, B and C are KA, KB and KC respectively. AC is the major axis and SB is perpendicular to AC at the position of the Sun S as shown in the figure. Then
Why is the energy of a satellite (or any other planet) negative?
Derive an expression for escape speed.
Derive the time period of the satellite orbiting the Earth.
Derive an expression for the energy of satellite.
In the following, what are the quantities which that are conserved?
If the Earth has no tilt, what happens to the seasons of the Earth?
An unknown planet orbits the Sun with a distance twice the semi-major axis distance of the Earth’s orbit. If the Earth’s time period is T1, what is the time period of this unknown planet?
Four particles, each of mass M and equidistant from each other, move along a circle of radius R under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction. Calculate the speed of each particle.
