Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain why (or how) Solids can support both longitudinal and transverse waves, but only longitudinal waves can propagate in gases
उत्तर १
Solids have shear modulus. They can sustain shearing stress. Since fluids do not have any definite shape, they yield to shearing stress. The propagation of a transverse wave is such that it produces shearing stress in a medium. The propagation of such a wave is possible only in solids, and not in gases.
Both solids and fluids have their respective bulk moduli. They can sustain compressive stress. Hence, longitudinal waves can propagate through solids and fluids.
उत्तर २
This is due to the fact that gases have only the bulk modulus of elasticity whereas solids have both, the shear modulus as well as the bulk modulus of elasticity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A transverse harmonic wave on a string is described by y(x, t) = 3.0 sin (36 t + 0.018 x + π/4)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. The positive direction of x is from left to right.
(a) Is this a travelling wave or a stationary wave?
If it is travelling, what are the speed and direction of its propagation?
(b) What are its amplitude and frequency?
(c) What is the initial phase at the origin?
(d) What is the least distance between two successive crests in the wave?
Explain the reflection of transverse and longitudinal waves from a denser medium and a rared medium.
You are walking along a seashore and a mild wind is blowing. Is the motion of air a wave motion?
Longitudinal waves cannot
Mark out the correct options.
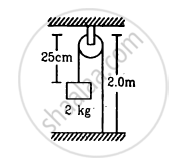
In the arrangement shown in figure , the string has a mass of 4⋅5 g. How much time will it take for a transverse disturbance produced at the floor to reach the pulley? Take g = 10 m s−2.
A circular loop of string rotates about its axis on a frictionless horizontal place at a uniform rate so that the tangential speed of any particle of the string is ν. If a small transverse disturbance is produced at a point of the loop, with what speed (relative to the string) will this disturbance travel on the string?
A tuning fork of frequency 440 Hz is attached to a long string of linear mass density 0⋅01 kg m−1 kept under a tension of 49 N. The fork produces transverse waves of amplitude 0⋅50 mm on the string. (a) Find the wave speed and the wavelength of the waves. (b) Find the maximum speed and acceleration of a particle of the string. (c) At what average rate is the tuning fork transmitting energy to the string?
A 660 Hz tuning fork sets up vibration in a string clamped at both ends. The wave speed for a transverse wave on this string is 220 m s−1 and the string vibrates in three loops. (a) Find the length of the string. (b) If the maximum amplitude of a particle is 0⋅5 cm, write a suitable equation describing the motion.
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = 3 sin (5x – 0.5t) + 4 cos (5x – 0.5t)
