Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Longitudinal waves cannot
विकल्प
have a unique wavelength
transmit energy
have a unique wave velocity
be polarized.
उत्तर
be polarised
A longitudinal wave has particle displacement along its direction of motion; thus, it cannot be polarised.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why (or how): Bats can ascertain distances, directions, nature, and sizes of the obstacles without any “eyes”,
Explain why (or how) Solids can support both longitudinal and transverse waves, but only longitudinal waves can propagate in gases
A transverse wave is produced on a stretched string 0.9 m long and fixed at its ends. Find the speed of the transverse wave, when the string vibrates while emitting the second overtone of frequency 324 Hz.
You are walking along a seashore and a mild wind is blowing. Is the motion of air a wave motion?
A mechanical wave propagates in a medium along the X-axis. The particles of the medium
(a) must move on the X-axis
(b) must move on the Y-axis
(c) may move on the X-axis
(d) may move on the Y-axis.
A particle on a stretched string supporting a travelling wave, takes 5⋅0 ms to move from its mean position to the extreme position. The distance between two consecutive particles, which are at their mean positions, is 2⋅0 cm. Find the frequency, the wavelength and the wave speed.
A steel wire of length 64 cm weighs 5 g. If it is stretched by a force of 8 N, what would be the speed of a transverse wave passing on it?
Two wires of different densities but same area of cross section are soldered together at one end and are stretched to a tension T. The velocity of a transverse wave in the first wire is double of that in the second wire. Find the ratio of the density of the first wire to that of the second wire.
An organ pipe, open at both ends, contains
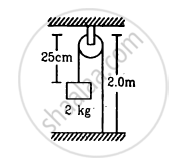
In the arrangement shown in figure , the string has a mass of 4⋅5 g. How much time will it take for a transverse disturbance produced at the floor to reach the pulley? Take g = 10 m s−2.
A transverse wave of amplitude 0⋅50 mm and frequency 100 Hz is produced on a wire stretched to a tension of 100 N. If the wave speed is 100 m s−1, what average power is the source transmitting to the wire?
A tuning fork of frequency 440 Hz is attached to a long string of linear mass density 0⋅01 kg m−1 kept under a tension of 49 N. The fork produces transverse waves of amplitude 0⋅50 mm on the string. (a) Find the wave speed and the wavelength of the waves. (b) Find the maximum speed and acceleration of a particle of the string. (c) At what average rate is the tuning fork transmitting energy to the string?
If the speed of a transverse wave on a stretched string of length 1 m is 60 m−1, what is the fundamental frequency of vibration?
A steel wire of mass 4⋅0 g and length 80 cm is fixed at the two ends. The tension in the wire is 50 N. Find the frequency and wavelength of the fourth harmonic of the fundamental.
A 660 Hz tuning fork sets up vibration in a string clamped at both ends. The wave speed for a transverse wave on this string is 220 m s−1 and the string vibrates in three loops. (a) Find the length of the string. (b) If the maximum amplitude of a particle is 0⋅5 cm, write a suitable equation describing the motion.
The equation of a standing wave, produced on a string fixed at both ends, is
\[y = \left( 0 \cdot 4 cm \right) \sin \left[ \left( 0 \cdot 314 {cm}^{- 1} \right) x \right] \cos \left[ \left( 600\pi s^{- 1} \right) t \right]\]
What could be the smallest length of the string?
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement (transverse or longitudinal) of an elastic wave. State which of these represent (i) a traveling wave, (ii) a stationary wave or (iii) none at all:
y = 3 sin (5x – 0.5t) + 4 cos (5x – 0.5t)
