Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the dimensions of linear momentum .
उत्तर
Linear momentum = mv
Here, [m] = [M] and [v] = [LT−1]
∴ Dimension of linear momentum, [mv] = [MLT−1]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
It is desirable that the standards of units be easily available, invariable, indestructible and easily reproducible. If we use foot of a person as a standard unit of length, which of the above features are present and which are not?
A unitless quantity
The dimensions ML−1 T−2 may correspond to
Find the dimensions of frequency .
Find the dimensions of pressure.
Find the dimensions of
(a) angular speed ω,
(b) angular acceleration α,
(c) torque τ and
(d) moment of interia I.
Some of the equations involving these quantities are \[\omega = \frac{\theta_2 - \theta_1}{t_2 - t_1}, \alpha = \frac{\omega_2 - \omega_1}{t_2 - t_1}, \tau = F . r \text{ and }I = m r^2\].
The symbols have standard meanings.
Find the dimensions of the specific heat capacity c.
(a) the specific heat capacity c,
(b) the coefficient of linear expansion α and
(c) the gas constant R.
Some of the equations involving these quantities are \[Q = mc\left( T_2 - T_1 \right), l_t = l_0 \left[ 1 + \alpha\left( T_2 - T_1 \right) \right]\] and PV = nRT.
Find the dimensions of the coefficient of linear expansion α and
Let I = current through a conductor, R = its resistance and V = potential difference across its ends. According to Ohm's law, product of two of these quantities equals the third. Obtain Ohm's law from dimensional analysis. Dimensional formulae for R and V are \[{\text{ML}}^2 \text{I}^{- 2} \text{T}^{- 3}\] and \[{\text{ML}}^2 \text{T}^{- 3} \text{I}^{- 1}\] respectively.
Test if the following equation is dimensionally correct:
\[V = \frac{\pi P r^4 t}{8 \eta l}\]
where v = frequency, P = pressure, η = coefficient of viscosity.
Test if the following equation is dimensionally correct:
\[v = \frac{1}{2 \pi}\sqrt{\frac{mgl}{I}};\]
where h = height, S = surface tension, \[\rho\] = density, P = pressure, V = volume, \[\eta =\] coefficient of viscosity, v = frequency and I = moment of interia.
If \[\vec{A} \times \vec{B} = 0\] can you say that
(a) \[\vec{A} = \vec{B} ,\]
(b) \[\vec{A} \neq \vec{B}\] ?
The component of a vector is
Let \[\vec{a} = 4 \vec{i} + 3 \vec{j} \text { and } \vec{b} = 3 \vec{i} + 4 \vec{j}\]. Find the magnitudes of (a) \[\vec{a}\] , (b) \[\vec{b}\] ,(c) \[\vec{a} + \vec{b} \text { and }\] (d) \[\vec{a} - \vec{b}\].
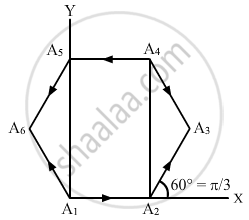
Let A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A1 be a regular hexagon. Write the x-components of the vectors represented by the six sides taken in order. Use the fact the resultant of these six vectors is zero, to prove that
cos 0 + cos π/3 + cos 2π/3 + cos 3π/3 + cos 4π/3 + cos 5π/3 = 0.
Use the known cosine values to verify the result.
If \[\vec{A} = 2 \vec{i} + 3 \vec{j} + 4 \vec{k} \text { and } \vec{B} = 4 \vec{i} + 3 \vec{j} + 2 \vec{k}\] find \[\vec{A} \times \vec{B}\].
If \[\vec{A} , \vec{B} , \vec{C}\] are mutually perpendicular, show that \[\vec{C} \times \left( \vec{A} \times \vec{B} \right) = 0\] Is the converse true?
High speed moving particles are studied under
