Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
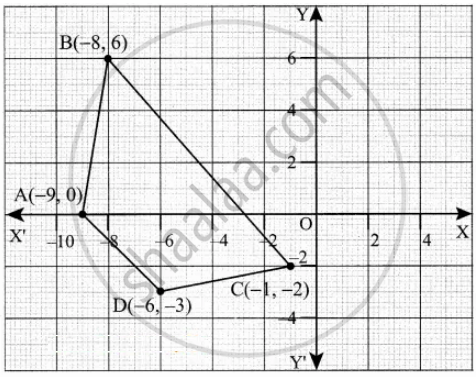
Find the area of the quadrilateral whose vertices are at (– 9, 0), (– 8, 6), (– 1, – 2) and (– 6, – 3)
उत्तर
Let the vertices A(– 9, 0), B(– 8, 6), C(– 1, –2) and D(– 6, – 3)
Plot the vertices in a graph and take them in counter-clockwise order.
Area of the Quadrilateral DCBA
= `1/2[(x_1y_2 + x_2y_3 + x_3y_4 + x_4y_1) - (x_2y_1 + x_3y_2 + x_4y_3 + x_1y_4)]`
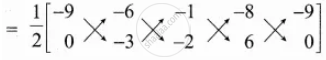
= `1/2[33 + 35]`
= `1/2 xx 68`
= 34 sq.units
Area of the Quadrilateral = 34 sq.units
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
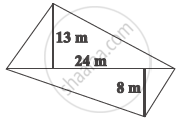
The diagonal of a quadrilateral shaped field is 24 m and the perpendiculars dropped on it from the remaining opposite vertices are 8 m and 13 m. Find the area of the field.
ABCD is a square with each side 12 cm. P is a point on BC such that area of ΔABP: area of trapezium APCD = 1: 5. Find the length of CP.
The following diagram shows a pentagonal field ABCDE in which the lengths of AF, FG, GH, and HD are 50 m, 40 m, 15 m and 25 m, respectively, and the lengths of perpendiculars BF, CH and EG are 50 m, 25 m and 60 m respectively. Determine the area of the field.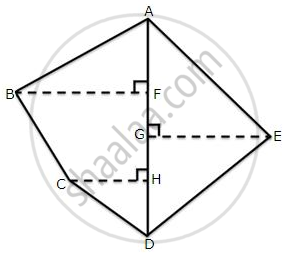
Find the area and perimeter of a square plot of land, the length of whose diagonal is 15 meters. Given your answer correct to 2 places of decimals.
Using the information in the following figure, find its area.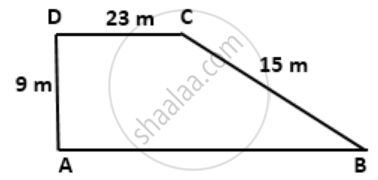
The floor of a room is of size 6 m x 5 m. Find the cost of covering the floor of the room with 50 cm wide carpet at the rate of Rs.24.50 per metre. Also, find the cost of carpeting the same hall if the carpet, 60 cm, wide, is at the rate of Rs.26 per metre.
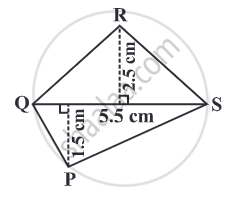
Find the area of quadrilateral PQRS.
Vertices of given triangles are taken in order and their areas are provided aside. Find the value of ‘p’.
| Vertices | Area (sq.units) |
| (p, p), (5, 6), (5, –2) | 32 |
In the following, find the value of ‘a’ for which the given points are collinear
(a, 2 – 2a), (– a + 1, 2a) and (– 4 – a, 6 – 2a)
Find the area of quadrilateral BCEG