Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Four particles having masses m, 2m, 3m and 4m are placed at the four corners of a square of edge a. Find the gravitational force acting on a particle of mass m placed at the centre.
उत्तर
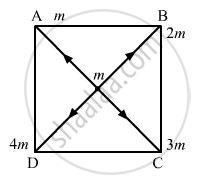
\[\text { Force due to the particle at A }, \overrightarrow{F}_{OA} = \frac{G \times m \times m}{{OA}^2}\]
\[\text { Let OA } = r\]
\[ \therefore \overrightarrow{F}_{OA} = \frac{G \times m \times m}{r^2} \]
\[\text { Here }, r = \sqrt{\left( \frac{a}{2} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{a}{2} \right)^2} = \frac{a}{\sqrt{2}}\]
\[\text { Force due to the particle at B }, \overrightarrow{F}_{OB} = \frac{G \times m \times 2m}{r^2}\]
\[\text { Force due to the particle at C }, \overrightarrow{F}_{OC} = \frac{G \times m \times 3m}{r^2}\]
\[\text { Force due to the particle at D }, \overrightarrow{F}_{OD} = \frac{G \times m \times 4m}{r^2}\]
\[\text { Now, resultant force }= \overrightarrow{F}_{OA} + \overrightarrow{F}_{OB} + \overrightarrow{F}_{OC} + \overrightarrow{F}_{OD} \]
\[ = \frac{2Gmm}{a^2}\left[ - \frac{\overrightarrow{i}}{\sqrt{2}} + \frac{\overrightarrow{j}}{\sqrt{2}} \right] + \frac{4Gmm}{a^2}\left[ \frac{\overrightarrow{i}}{\sqrt{2}} + \frac{\overrightarrow{j}}{\sqrt{2}} \right]\]
\[ = \frac{6Gmm}{a^2}\left[ \frac{\overrightarrow{i}}{\sqrt{2}} - \frac{\vec{j}}{\sqrt{2}} \right] + \frac{8Gmm}{a^2}\left[ \frac{- \overrightarrow{i}}{\sqrt{2}} - \frac{- \overrightarrow{j}}{\sqrt{2}} \right]\]
\[ \therefore F = \frac{4\sqrt{4}G m^2}{a^2} \stackrel\frown {j}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
Answer the following:
An astronaut inside a small space ship orbiting around the earth cannot detect gravity. If the space station orbiting around the earth has a large size, can he hope to detect gravity?
Can we apply Newton’s third law to the gravitational force ? Explain your answer.
At noon, the sun and the earth pull the objects on the earth's surface in opposite directions. At midnight, the sun and the earth pull these objects in same direction. Is the weight of an object, as measured by a spring balance on the earth's surface, more at midnight as compared to its weight at noon?
Let V and E represent the gravitational potential and field at a distance r from the centre of a uniform solid sphere. Consider the two statements:
(A) the plot of V against r is discontinuous.
(B) The plot of E against r is discontinuous.
A tunnel is dug along a diameter of the earth. Find the force on a particle of mass m placed in the tunnel at a distance x from the centre.
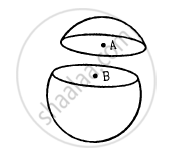
A thin spherical shell having uniform density is cut in two parts by a plane and kept separated as shown in the following figure. The point A is the centre of the plane section of the first part and B is the centre of the plane section of the second part. Show that the gravitational field at A due to the first part is equal in magnitude to the gravitational field at B due to the second part.
The gravitational field in a region is given by \[E = \left( 2 \overrightarrow{i} + 3 \overrightarrow{j} \right) N {kg}^{- 1}\] . Show that no work is done by the gravitational field when a particle is moved on the line 3y + 2x = 5.
[Hint : If a line y = mx + c makes angle θ with the X-axis, m = tan θ.]
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It goes to a height 20 m and then returns to the ground. Taking acceleration due to gravity g to be 10 ms-2, find: the initial velocity of the ball.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The mass of earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of earth is 6.4 × 106 m. The magnitude of force between the mass of 1 kg and the earth is:
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case:
Hammering a nail.
What is the difference between gravity and gravitation?
Answer the following question.
State Newton’s law of gravitation and express it in vector form.
Mahendra and Virat are sitting at a distance of 1 m from each other.Their masses are 75 kg and 80 kg respectively. What is the gravitational force between them? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2/kg2)
Law of gravitation gives the gravitational force between
As observed from earth, the sun appears to move in an approximate circular orbit. For the motion of another planet like mercury as observed from earth, this would ______.
If three equal masses m are placed at the three vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 1/m then what force acts on a particle of mass 2m placed at the centroid?
