Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give the structure of the product you would expect when the following alcohol reacts with HCl–ZnCl2.
Butan-1-ol
उत्तर
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2CH2OH + HCl_{(conc.)}->[ZnCl2]No reaction at room temperature}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain how does the −OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activate it towards electrophilic substitution?
Account for the following:
o-nitrophenol is more steam volatile than p-nitrophenol.
Phenols do not react with one of the following:
Acidity of phenol is due to ____________.
The ionization constant of phenol is higher than that of ethanol because ____________.
In CH3CH2OH, the bond that undergoes heterolytical change most readily is ____________.
Strength of acidity is in order:
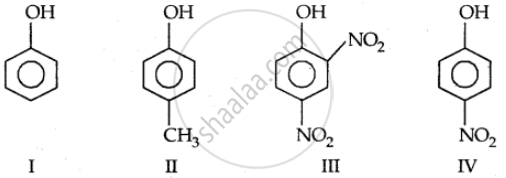
Which of the following compounds is most acidic?
What is the correct order of reactivity of alcohols in the following reaction?
\[\ce{R-OH + HCl ->[ZnCl2] R-Cl + H2O}\]
Which of the following statements is true:
Assertion: o-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than the m- and p-isomers.
Reason: m- and p- Nitrophenols exist as associated molecules.
In the following compounds:
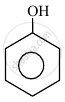 |
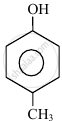 |
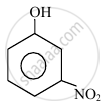 |
 |
| (I) | (II) | (III) | (IV) |
The order to acidity is ______.
For the pair phenol and cyclohexanol, answer the following:
Why is phenol more acidic than cyclohexanol?
Give the structure of the product you would expect when the following alcohol reacts with HCl–ZnCl2.
2-Methylbutan-2-ol
Give the structure of the product you would expect when the following alcohol reacts with HBr.
Butan-1-ol
Give the structure of the product you would expect when the following alcohol reacts with HBr.
2-Methylbutan-2-ol
Give the structure of the product you would expect when the following alcohol reacts with SOCl2.
Butan-1-ol
