Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Given reasons: C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C–Cl bond length in CH3–Cl.
उत्तर
In chlorobenzene, the C−Cl bond gets partial double bond character because of the +M effect shown by the Cl group. Due to double bond character, the bond length decreases in chlorobenzene as compared to the normal CH3−Cl bond length. Therefore, the C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than the C–Cl bond length in CH3–Cl.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane.
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH(Br)CH2CH3 + NaOH ->[water]}\]
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 ->}\]
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide
alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide.
Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched?
| Reaction | Product | |
| I | RX + AgCN | RNC |
| II | RX + KCN | RCN |
| III | RX + KNO2 | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{.......}\ce{O}\\ \phantom{.....}/\\ \ce{R - N}\phantom{....}\\ \phantom{.....}\backslash\backslash\\ \phantom{.......}\ce{O} \end{array}\] |
| IV | RX + AgNO2 | \[\ce{R-O-N=O}\] |
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for an SN2 reaction is:
Which of the following compounds is optically active?
Write the structures and names of the compounds formed when compound ‘A’ with molecular formula, \[\ce{C7H8}\] is treated with \[\ce{Cl2}\] in the presence of \[\ce{FeCl3}\].
Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution. Predict and explain the order of reactivity of the following compounds towards nucleophilic substitution:
| (I) | 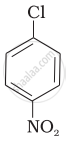 |
| (II) | 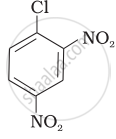 |
| (III) | 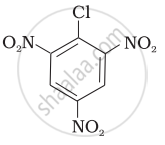 |
Which of the following compounds will show retention in configuration on nucleophile substitution by OH− ion?
