Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the structure of the major organic product in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 ->}\]
उत्तर
\[\ce{\underset{Propan-1-ol}{CH3CH2CH2OH} + SOCl2 ->[nucleophilic substitution] \underset{1-Chloropropane}{CH3CH2CH2Cl} + HCl\uparrow + SO2\uparrow}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane.
Given reasons: C–Cl bond length in chlorobenzene is shorter than C–Cl bond length in CH3–Cl.
Write the structure of the major product in each of the following reaction :
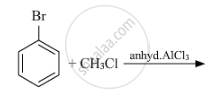
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
\[\ce{{n}BuBr + KCN ->[EtOH-H2O] {n}BuCN}\]
The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in the presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain.
Which would undergo SN2 reaction faster in the following pair and why ?
CH3 – CH2 – Br and CH3 – CH2 – I
What is the action of the following on ethyl bromide:
silver acetate
Arrange the following organic compounds in descending order of their reactivity towards SN1 reaction.
C6H5CH2Br, C6H5CH(C6H5)Br, C6H5CH(CH3)Br, C6H5C(CH3)(C6H5)Br
Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched?
| Reaction | Product | |
| I | RX + AgCN | RNC |
| II | RX + KCN | RCN |
| III | RX + KNO2 | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{.......}\ce{O}\\ \phantom{.....}/\\ \ce{R - N}\phantom{....}\\ \phantom{.....}\backslash\backslash\\ \phantom{.......}\ce{O} \end{array}\] |
| IV | RX + AgNO2 | \[\ce{R-O-N=O}\] |
Which one of the following halogen compounds is difficult to be hydrolysed by SN1 mechanism?
Most reactive halide towards SN1 reaction is ____________.
SN1 reaction of alkyl halides lead to ___________.
Identify X and Y in the following sequence:
\[\ce{C2H5Br ->[X] Product ->[Y] C3H7NH2}\]
The correct order of increasing the reactivity of C–X bond towards nucleophile in following compounds.
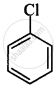
(I)
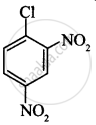
(II)
(CH3)3CCl
(III)
(CH3)2CHCl
(IV)
Assertion: KCN reacts with methyl chloride to give methyl isocyanide.
Reason: CN– is an ambident nucleophile.
Compound ‘A’ with molecular formula \[\ce{C4H9Br}\] is treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound ‘A’ only. When another optically active isomer ‘B’ of this compound was treated with aq. \[\ce{KOH}\] solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on concentration of compound and \[\ce{KOH}\] both.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be converted to the product with inverted configuration.
Which one of the following compounds is more reactive towards SN1 reaction?
Give reason for the following:
The product formed during SN1 reaction is a racemic mixture.
An organic compound A with the molecular formula (+) C4H9Br undergoes hydrolysis to form (+) C4H9OH. Give the structure of A and write the mechanism of the reaction.
Explain why Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
