Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Identify the nature of the radioactive radiations emitted in each step of the decay process given below.
उत्तर
An alpha particle
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
Using the equation
Why is it experimentally found difficult to detect neutrinos in this process ?
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the beta particle emitted in the following decay scheme:
12N → 12C* + e+ + v
12C* → 12C + γ (4.43MeV).
The atomic mass of 12N is 12.018613 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
When charcoal is prepared from a living tree, it shows a disintegration rate of 15.3 disintegrations of 14C per gram per minute. A sample from an ancient piece of charcoal shows 14C activity to be 12.3 disintegrations per gram per minute. How old is this sample? Half-life of 14C is 5730 y.
Define one Becquerel.
'Half-life' of a radioactive substance accounts for ______.
What percentage of radioactive substance is left after five half-lives?
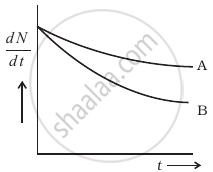
Which sample, A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?