Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the quadrilateral formed by joining the mid-points of the adjacent sides of quadrilateral ABCD is a rectangle,
show that the diagonals AC and BD intersect at the right angle.
उत्तर
The figure is shown below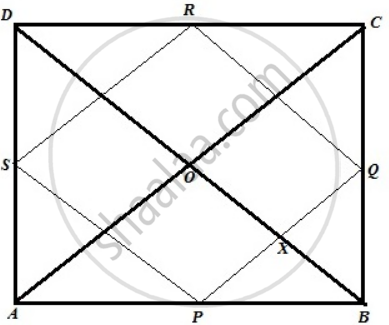
Let ABCD be a quadrilateral where P, Q, R, S are the midpoint of AB, BC, CD, DA.PQRS is a rectangle. Diagonal AC and BD intersect at point O. We need to show that AC and BD intersect at a right angle.
Proof:
PQ || AC, therefore ∠AOD = ∠PXO ...[ Corresponding angle ]...(1)
Again BD || RQ, therefore ∠PXO = ∠RQX = 90° ....[ Corresponding angle and angle of a rectangle ]...(2)
From (1) and (2) we get ,
∠AOD = 90°
Similarly, ∠AOB = ∠BOC = ∠DOC = 90°
Therefore diagonals AC and BD intersect at right angle.
Hence proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
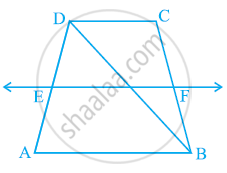
ABCD is a trapezium in which AB || DC, BD is a diagonal and E is the mid-point of AD. A line is drawn through E parallel to AB intersecting BC at F (see the given figure). Show that F is the mid-point of BC.
ABC is a triangle right angled at C. A line through the mid-point M of hypotenuse AB and parallel to BC intersects AC at D. Show that
- D is the mid-point of AC
- MD ⊥ AC
- CM = MA = `1/2AB`
Let Abc Be an Isosceles Triangle in Which Ab = Ac. If D, E, F Be the Mid-points of the Sides Bc, Ca and a B Respectively, Show that the Segment Ad and Ef Bisect Each Other at Right Angles.
In triangle ABC, M is mid-point of AB and a straight line through M and parallel to BC cuts AC in N. Find the lengths of AN and MN if Bc = 7 cm and Ac = 5 cm.
The following figure shows a trapezium ABCD in which AB // DC. P is the mid-point of AD and PR // AB. Prove that:
PR = `[1]/[2]` ( AB + CD)

In trapezium ABCD, AB is parallel to DC; P and Q are the mid-points of AD and BC respectively. BP produced meets CD produced at point E.
Prove that:
- Point P bisects BE,
- PQ is parallel to AB.
In a right-angled triangle ABC. ∠ABC = 90° and D is the midpoint of AC. Prove that BD = `(1)/(2)"AC"`.
In the given figure, ABCD is a trapezium. P and Q are the midpoints of non-parallel side AD and BC respectively. Find: AB, if DC = 8 cm and PQ = 9.5 cm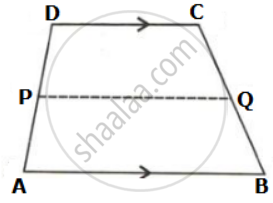
In AABC, D and E are two points on the side AB such that AD = DE = EB. Through D and E, lines are drawn parallel to BC which meet the side AC at points F and G respectively. Through F and G, lines are drawn parallel to AB which meet the side BC at points M and N respectively. Prove that BM = MN = NC.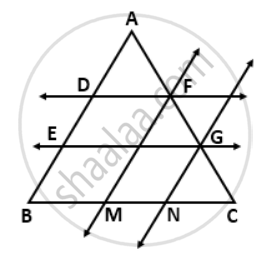
P, Q, R and S are respectively the mid-points of the sides AB, BC, CD and DA of a quadrilateral ABCD in which AC = BD. Prove that PQRS is a rhombus.
