Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In following cases, determine the direction cosines of the normal to the plane and the distance from the origin.
2x + 3y – z = 5
उत्तर
2x + 3y − z = 5 … (1)
The direction ratios of normal are 2, 3, and −1.
`:.sqrt((2)^2 + (3)^3 + (-1)^2) = sqrt(14)`
Dividing both sides of equation (1) by `sqrt14`, we obtain
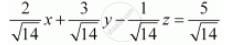
This equation is of the form lx + my + nz = d, where l, m, n are the direction cosines of normal to the plane and d is the distance of normal from the origin.
Therefore, the direction cosines of the normal to the plane are `2/sqrt14, 3/sqrt14 and (-1)/sqrt(14)` the distance of normal from the origin is `5/sqrt14` units.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In following cases, determine the direction cosines of the normal to the plane and the distance from the origin.
x + y + z = 1
If the coordinates of the points A, B, C, D be (1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 7), (−4, 3, −6) and (2, 9, 2) respectively, then find the angle between the lines AB and CD.
Find the coordinates of the point where the line through (5, 1, 6) and (3, 4, 1) crosses the YZ-plane
Find the coordinates of the point where the line through (5, 1, 6) and (3, 4, 1) crosses the ZX − plane.
Find the coordinates of the point where the line through (3, −4, −5) and (2, − 3, 1) crosses the plane 2x + y + z = 7).
The planes: 2x − y + 4z = 5 and 5x − 2.5y + 10z = 6 are
(A) Perpendicular
(B) Parallel
(C) intersect y-axis
(C) passes through `(0,0,5/4)`
Find the coordinates of the point where the line through the points (3, - 4, - 5) and (2, - 3, 1), crosses the plane determined by the points (1, 2, 3), (4, 2,- 3) and (0, 4, 3)
If the axes are rectangular and P is the point (2, 3, −1), find the equation of the plane through P at right angles to OP.
Find the intercepts made on the coordinate axes by the plane 2x + y − 2z = 3 and also find the direction cosines of the normal to the plane.
Reduce the equation \[\vec{r} \cdot \left( \hat{i} - 2 \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} \right) + 6 = 0\] to normal form and, hence, find the length of the perpendicular from the origin to the plane.
Write the normal form of the equation of the plane 2x − 3y + 6z + 14 = 0.
The direction ratios of the perpendicular from the origin to a plane are 12, −3, 4 and the length of the perpendicular is 5. Find the equation of the plane.
Find a unit normal vector to the plane x + 2y + 3z − 6 = 0.
Find the equation of a plane which is at a distance of \[3\sqrt{3}\] units from the origin and the normal to which is equally inclined to the coordinate axes.
Find the equation of the plane which contains the line of intersection of the planes \[x + 2y + 3z - 4 = 0 \text { and } 2x + y - z + 5 = 0\] and whose x-intercept is twice its z-intercept.
Prove that the line of section of the planes 5x + 2y − 4z + 2 = 0 and 2x + 8y + 2z − 1 = 0 is parallel to the plane 4x − 2y − 5z − 2 = 0.
Find the value of λ such that the line \[\frac{x - 2}{6} = \frac{y - 1}{\lambda} = \frac{z + 5}{- 4}\] is perpendicular to the plane 3x − y − 2z = 7.
Find the equation of the plane passing through the points (−1, 2, 0), (2, 2, −1) and parallel to the line \[\frac{x - 1}{1} = \frac{2y + 1}{2} = \frac{z + 1}{- 1}\]
Write a vector normal to the plane \[\vec{r} = l \vec{b} + m \vec{c} .\]
Write the value of k for which the line \[\frac{x - 1}{2} = \frac{y - 1}{3} = \frac{z - 1}{k}\] is perpendicular to the normal to the plane \[\vec{r} \cdot \left( 2 \hat{i} + 3 \hat{j} + 4 \hat{k} \right) = 4 .\]
Write the vector equation of the line passing through the point (1, −2, −3) and normal to the plane \[\vec{r} \cdot \left( 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k} \right) = 5 .\]
If the line drawn from the point (–2, – 1, – 3) meets a plane at right angle at the point (1, – 3, 3), find the equation of the plane.
The unit vector normal to the plane x + 2y +3z – 6 = 0 is `1/sqrt(14)hat"i" + 2/sqrt(14)hat"j" + 3/sqrt(14)hat"k"`.
What will be the cartesian equation of the following plane. `vecr * (hati + hatj - hatk)` = 2
Find the vector and cartesian equations of the planes that passes through (1, 0, – 2) and the normal to the plane is `hati + hatj - hatk`
