Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the given figure, ABCD is a rectangle in which diagonal AC is produced to E. If ∠ECD = 146°, find ∠AOB.
उत्तर
ABCD is a rectangle
With diagonal AC produced to point E.
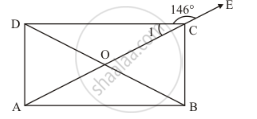
We have
∠1 + ∠DCE = 180° (Linear pair)
∠1 + 146° = 180°
∠1 = 34°
We know that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
Thus OC = OD
Also, angles opposite to equal sides are equal.
Therefore,
∠ODC = 34°
By angle sum property of a traingle
∠ODC +∠1 + COD = 180°
34° + 34° CPD = 180°
68° +∠COD = 180°
∠COD = 112°
Also, ∠CODand ∠AOB are vertically opposite angles.
Therefore, ∠AOB = 112°
Hence, the required measure for ∠AOBis 112°.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
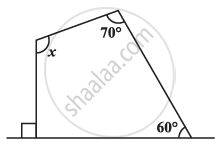
Find the angle measure x in the given Figure
In a quadrilateral ABCD, the angles A, B, C and D are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 4 : 5. Find the measure of each angles of the quadrilateral
If the angles of a quadrilateral are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 9 : 13, then find the measure of the smallest angle.
In a quadrilateral ABCD, bisectors of angles A and B intersect at O such that ∠AOB = 75°, then write the value of ∠C + ∠D.
In the given figure, PQRS is a rhombus in which the diagonal PR is produced to T. If ∠SRT = 152°, find x, y and z.

If the diagonals of a rhombus are 18 cm and 24 cm respectively, then its side is equal to
In a rhombus ABCD, if ∠ACB = 40°, then ∠ADB =
In the following figure, P is the mid-point of side BC of a parallelogram ABCD such that ∠BAP = ∠DAP. Prove that AD = 2CD.

A quadrilateral has three acute angles. If each measures 80°, then the measure of the fourth angle is ______.
In a quadrilateral PQRS, ∠P = 50°, ∠Q = 50°, ∠R = 60°. Find ∠S. Is this quadrilateral convex or concave?
