Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Is it always possible to see the photoelectric effect with a red light?
उत्तर
No, it is not possible to see the photoelectric effect with a red light.
Explanation:
The energy required to rip an electron out of its orbital is equal to the electron's work function, and photons in red light lack this energy. Because light behaves like particles rather than a continuous stream, even very high-intensity red light will never be able to overcome an electron's work function (in this case), because each photon fails to do so. This demonstrates the particle behaviour of light. The photoelectric effect demonstrates the particle nature of light, and even very intense or prolonged exposure to red light will not cause the effect if the photon energy is insufficient.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
Polychromatic (containing many different frequencies) radiation is used in an experiment on the photoelectric effect. The stopping potential ______.
What is the photoelectric effect?
Can microwaves be used in the experiment on photoelectric effect?
It is observed in an experiment on the photoelectric effect that an increase in the intensity of the incident radiation does not change the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons. Where does the extra energy of the incident radiation go? Is it lost? State your answer with explanatory reasoning.
Photocurrent recorded in the microammeter in an experimental setup of the photoelectric effect vanishes when the retarding potential is more than 0.8 V if the wavelength of incident radiation is 4950 Å. If the source of incident radiation is changed, the stopping potential turns out to be 1.2 V. Find the work function of the cathode material and the wavelength of the second source.
The minimum frequency for photoelectric effect on metal is 7 × 1014 Hz, Find the work function of the metal.
Find the kinetic energy of the emitted electron, if in photoelectric effect energy of incident Photon is 4 eV and work function is 2.4 eV.
State Einstein’s photoelectric equation. Explain all characteristics of the photoelectric effect, on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
The energy of the incident photon on the metal surface is 3 W and then 5 W, where W is the work function for that metal. The ratio of velocities of emitted photoelectrons is ______.
The maximum velocity of photoelectron emitted is 4.8 m/s. If the e/m ratio of the electron is 1.76 × 1011 C/kg, then stopping potential is given by ______
The ratio of energies of photons produced due to transition of electron of hydrogen atom from its (i) second to first energy level and (ii) highest energy level to second level is respectively.
The following graph shows the stopping potential V0 versus frequency v for photoelectric emission from two metals A and B. The slope of each of the lines gives ______
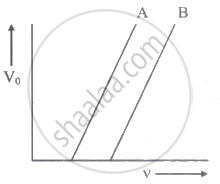
If the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons in photoelectric effect is 3.2 × 10-19 J and the work-function for metal is 6.63 × 10-19 J, then stopping potential and threshold wavelength respectively are
[Planck's constant, h = 6.63 × 1034 J-s]
[Velocity of light, c = 3 × 108 `"m"/"s"`]
[Charge on electron= 1.6 × 10-19 C]
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is 'v '. Charge and mass of the photoelectron is denoted by 'e' and 'm' respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
Threshold frequency for a metal is 1015 Hz. Light of `lambda` = 4000 Å falls on its surface. Which of the following statements is correct?
A metal surface is illuminated by photons of energy 5 eV and 2.5 eV respectively. The ratio of their wavelengths is ____________.
When light of wavelength 'λ' is incident on a photosensitive surface, the stopping potential is 'V'. When light of wavelength '3λ' is incident on the same surface, the stopping potential is `"V"/6`. Threshold wavelength for the surface is _______.
The photo electric effect to take place for a metal, the minimum frequency required is 5.792 × 1014 Hz. A light of wavelength 6000 Å is incident on that metal surface. What is the corresponding frequency of light and will there be photoelectric emissions? [velocity of light = 3 × 108 m/s]
Light of different frequencies, whose photons have energies 3 eV and 18 eV respectively, successively illuminate a metal of work function 2 eV. The ratio of the maximum speeds of the emitted electrons will be ______.
The photon of frequency vis incident on a metal surface whose threshold frequency is v0. The kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons will be ____________.
The lowest frequency of light that will cause the emission of photoelectrons from the surface of a metal (for which work function is 1.65 eV) will be ____________.
The work function of a photosensitive material is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photon emission from the substance is (approximately) ____________.
When a photosensitive surface is irradiated by lights of wavelengths `lambda_1` and `lambda_2`, kinetic energies of emitted photoelectrons are E1 and E2 respectively. The work function of the photosensitive surface is ____________.
Two incident radiations having energies two times and ten times of the work function of a metal surface, produce photoelectric effect. The ratio of maximum velocities of emitted photo electrons respectively is ____________.
The photoelectric threshold for a certain metal surface is 3600 Å. If the metal surface is irradiated by a wavelength of 1100 Å, then kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is ______.
Explain the failure of wave theory of light to account for the observations from experiments on photoelectric effect.
Give Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect.
By increasing the voltage in an electron diffraction tube, the radius of the diffraction rings will ______.
Explain the formation of clouds at high altitude.
