Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the following sets for all sets A, B, and C.
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) ((A′ ∪ B′) – A)′ | (a) A – B |
| (ii) [B′ ∪ (B′ – A)]′ | (b) A |
| (iii) (A – B) – (B – C) | (c) B |
| (iv) (A – B) ∩ (C – B) | (d) (A × B) ∩ (A × C) |
| (v) A × (B ∩ C) | (e) (A × B) ∪ (A × C) |
| (vi) A × (B ∪ C) | (f) (A ∩ C) – B |
उत्तर
| Column A | Answer |
| (i) ((A′ ∪ B′) – A)′ | (b) A |
| (ii) [B′ ∪ (B′ – A)]′ | (c) B |
| (iii) (A – B) – (B – C) | (a) A – B |
| (iv) (A – B) ∩ (C – B) | (f) (A ∩ C) – B |
| (v) A × (B ∩ C) | (d) (A × B) ∩ (A × C) |
| (vi) A × (B ∪ C) | (e) (A × B) ∪ (A × C) |
Explanation:
(i) ((A′ ∪ B′) – A)′
[(A′ ∪ B′) – A]′
= [(A′ ∪ B′) ∩ A’]’ ......{∵ A – B = A ∩ B’}
= [(A ∩ B)’ ∩ A’]’ ......{∵ (A ∩ B)’ = A’ ∪ B’}
= [(A ∩ B)’]’ ∪ (A’)’
= (A ∩ B) ∪ A
= A
((A′ ∪ B′) – A)′ = A
(ii) [B′ ∪ (B′ – A)]′
[B′ ∪ (B′ – A)]′
= (B’)’ ∩ (B’ – A)’ ......{∵ (A ∪ B)’ = A’ ∩ B’}
= B ∩ (B’ ∩ A’)’ ......{∵ A – B = A ∩ B’}
= B ∩ [(B’)’ ∪ (A’)’] ......{∵ (A ∩ B)’ = A’ ∪ B’}
= B ∩ (B ∪ A)
= B
[B′ ∪ (B′ – A)]′ = B
(iii) (A – B) – (B – C)
Step 1:
A – B
Step 2: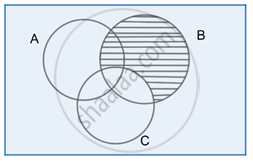
B – C
Step 3: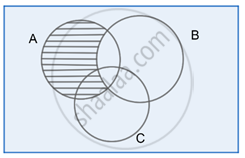
(A – B) – (B – C)
Clearly, the Venn diagram in Step 3 shows same region as in Step 1
Hence, (A – B) – (B – C) = A – B
(iv) (A – B) ∩ (C – B)
Step 1: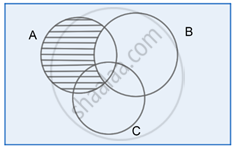
A – B
Step 2: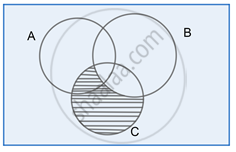
C – B
Step 3: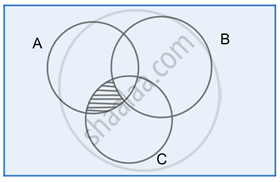
(A – B) ∩ (B – C)
Clearly, from the Venn diagram in Step 3:
(A – B) ∩ (B – C) = A ∩ C – B
(v) A × (B ∩ C)
Let y ∈ A × (B ∩ C)
⇒ y ∈ A and y ∈ (B ∩ C)
⇒ y ∈ A and (y ∈ B and y ∈ C)
⇒ (y ∈ A and y ∈ B) and (y ∈ A and y ∈ C)
⇒ y ∈ (A × B) and y ∈ (A × C)
⇒ y ∈ (A × B) ∩ (A × C)
A × (B ∩ C) = (A × B) ∩ (A × C)
(vi) A × (B ∪ C)
Let y ∈ A × (B ∪ C)
⇒ y ∈ A and y ∈ (B ∪ C)
⇒ y ∈ A and (y ∈ B or y ∈ C)
⇒ (y ∈ A and y ∈ B) or (y ∈ A and y ∈ C)
⇒ y ∈ (A × B) or y ∈ (A × C)
⇒ y ∈ (A × B) ∪ (A × C)
A × (B ∪ C) = (A × B) ∪ (A × C)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What universal set (s) would you propose for the following:
The set of isosceles triangles.
Given the sets, A = {1, 3, 5}, B = {2, 4, 6} and C = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8}, the following may be considered as universal set (s) for all the three sets A, B and C?
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Given the sets, A = {1, 3, 5}, B = {2, 4, 6} and C = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8}, the following may be considered as universal set (s) for all the three sets A, B and C?
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
If \[X = \left\{ 8^n - 7n - 1: n \in N \right\} \text{ and } Y = \left\{ 49\left( n - 1 \right): n \in N \right\}\] \[X \subseteq Y .\]
If U = {2, 3, 5, 7, 9} is the universal set and A = {3, 7}, B = {2, 5, 7, 9}, then prove that:
\[\left( A \cup B \right)' = A' \cap B'\]
For any two sets A and B, prove that
A ∩ B ⊂ A
For any two sets A and B, prove that A ⊂ B ⇒ A ∩ B = A
If A and B are sets, then prove that \[A - B, A \cap B \text{ and } B - A\] are pair wise disjoint.
Using properties of sets, show that for any two sets A and B,\[\left( A \cup B \right) \cap \left( A \cap B' \right) = A\]
Show that for any sets A and B, A = (A ∩ B) ∪ ( A - B)
Each set X, contains 5 elements and each set Y, contains 2 elements and \[\cup^{20}_{r = 1} X_r = S = \cup^n_{r = 1} Y_r\] If each element of S belong to exactly 10 of the Xr's and to eactly 4 of Yr's, then find the value of n.
For any two sets A and B, prove that :
\[A' - B' = B - A\]
For any two sets A and B, prove the following:
\[A \cap \left( A' \cup B \right) = A \cap B\]
For any two sets A and B, prove the following:
\[A - \left( A - B \right) = A \cap B\]
Let A and B be two sets such that : \[n \left( A \right) = 20, n \left( A \cup B \right) = 42 \text{ and } n \left( A \cap B \right) = 4\] \[n \left( A - B \right)\]
A survey shows that 76% of the Indians like oranges, whereas 62% like bananas. What percentage of the Indians like both oranges and bananas?
In a group of 950 persons, 750 can speak Hindi and 460 can speak English. Find:
how many can speak English only.
Let U be the universal set containing 700 elements. If A, B are sub-sets of U such that \[n \left( A \right) = 200, n \left( B \right) = 300 \text{ and } \left( A \cap B \right) = 100\].Then \[n \left( A' \cap B' \right) =\]
If A = {1, 2, 3, 4}, B = {3, 4, 5, 6}, C = {5, 6, 7, 8} and D = {7, 8, 9, 10}; find
B ∪ C
If X and Y are subsets of the universal set U, then show that X ⊂ Y ⇒ X ∩ Y = X
If A and B are subsets of the universal set U, then show that (A ∩ B) ⊂ A
In a survey of 200 students of a school, it was found that 120 study Mathematics, 90 study Physics and 70 study Chemistry, 40 study Mathematics and Physics, 30 study Physics and Chemistry, 50 study Chemistry and Mathematics and 20 none of these subjects. Find the number of students who study all the three subjects.
If A = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17} B = {2, 4, ..., 18} and N the set of natural numbers is the universal set, then A′ ∪ (A ∪ B) ∩ B′) is ______.
Given the sets A = {1, 3, 5}. B = {2, 4, 6} and C = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8}. Then the universal set of all the three sets A, B and C can be ______.
