Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Name the following diagram and explain the concept behind it.
उत्तर
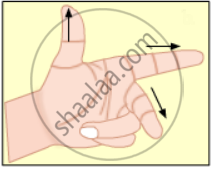
Fleming's left hand rule
It represents Fleming's left-hand rule used for finding the direction of magnetic force when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field.
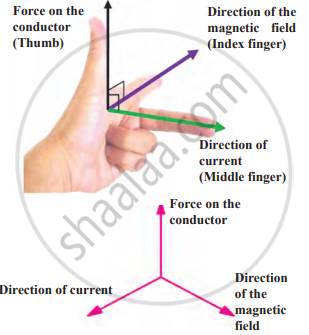
According to this rule, the left-hand thumb, index finger, and middle finger are stretched so as to be perpendicular to each other. If the index finger is in the direction of the magnetic field and the middle finger points in the direction of the current, then the direction of the thumb is the direction of the force on the conductor.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
State whether the following statement is true or false
The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
State qualitatively the effect of inserting an iron core into a current-carrying solenoid.
Name the rule for finding the direction of magnetic field produced by a straight current-carrying conductor.
State whether the following statement is true or false:
The magnetic field inside a long circular coil carrying current well be parallel straight lines.
Draw a sketch to show the magnetic lines of force due to a current-carrying straight conductor.
Draw the magnetic lines of force due to a circular wire carrying current.
Name the type of magnet with which the magnetic field pattern of a current-carrying solenoid resembles
A soft iron bar is inserted inside a current-carrying solenoid. The magnetic field inside the solenoid:
(a) will decrease
(b) will increase
(c) will become zero
(d) will remain the same
The front face of a circular wire carrying current behaves like a north pole. The direction of current in this face of circular wire is:
(a) clockwise
(b) downwards
(c) anticlockwise
(d) upwards
A current-carrying conductor is held in exactly vertical direction. In order to produce a clockwise magnetic field around the conductor, the current should passed in the conductor:
(a) from top towards bottom
(b) from left towards right
(c) from bottom towards top
(d) from right towards left
What happens when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field?
In a statement of Fleming's left-hand rule, what do the following represent?
(a) direction of centre finger.
(b) direction of forefinger.
(c) direction of thumb.
For Fleming's left-hand rule, write down the three things that are 90° to each other, and next to each one write down the finger or thumb that represents it.
A current-carrying conductor is placed perpendicularly in a magnetic field. Name the rule which can be used to find the direction of force acting on the conductor.
The force exerted on a current-carrying wire placed in a magnetic field is zero when the angle between the wire and the direction of magnetic field is:
45°
60°
90°
180°
A current flows in a wire running between the S and N poles of a magnet lying horizontally as shown in Figure below:
The force on the wire due to the magnet is directed:

fron N to S
from S to N
vertically downwards
vertically upwards
A horizontal wire carries a current as shown in Figure below between magnetic poles N and S:

Is the direction of the force on the wire due to the magnet:
(a) in the direction the current
(b) vertically downwards
(c) opposite to the current direction
(d) vertically upwards
What is the force on a current-carrying wire that is parallel to a magnetic field? Give reason for your answer.
State the unit of magnetic field in terms of the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field
A flat coil ABCD is freely suspended between the pole of U-shaped permanent magnet with the plane of coil parallel to the magnetic field.
What happens when a current is passed in the coil?
i) Which principle is explained in this figure?
ii) Which rule is used to find out the direction of a force in this principle?
iii) In which machine this principle is used? Draw a diagram showing working of that machine
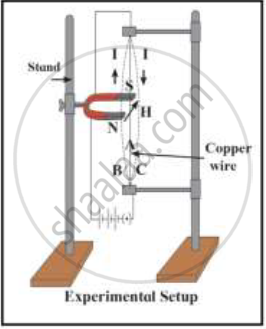
State Fleming's left handle rule.
State under what conditions force acting on a current carrying conductor which is freely suspended in a magnetic field can be Zero.
When current is parallel to a magnetic field, then force experience by the current-carrying conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field is ____________.
A simple motor is made in a school laboratory. A coil of wire is mounted on an axle between the poles of a horseshoe magnet, as illustrated.
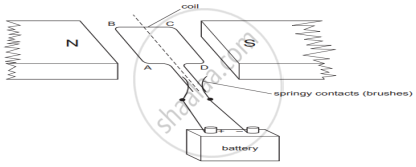
In the example above, coil ABCD is horizontal and the battery is connected as shown.
- For this position, state the direction of the force on the arm AB.
- Why does the current in the arm BC not contribute to the turning force on the coil?
A current-carrying conductor of a certain length, kept perpendicular to the magnetic field experiences a force F. What will be the force if the current is increased four times, the length is halved and the magnetic field is tripled?
A copper wire is held between the poles of a magnet
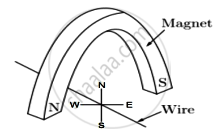
The current in the wire can be reversed. The pole of the magnet can also be changed over. In how many of the four directions shown can the force act on the wire?
Which of the following pattern correctly describes the magnetic field around a long straight wire carrying current?
Assertion (A): A current carrying straight conductor experiences a force when placed perpendicular to the direction of magnetic field.
Reason (R): The net charge on a current carrying conductor is always zero.
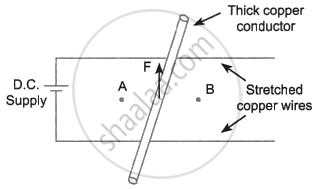
A copper conductor is placed over two stretched copper wires whose ends ate connected to a D.C. supply as shown in the diagram.
- What should be the magnetic poles at the points A and B lying on either side of the conductor to experience the force in the upward direction?
- Name the law used to find these polarities.
|
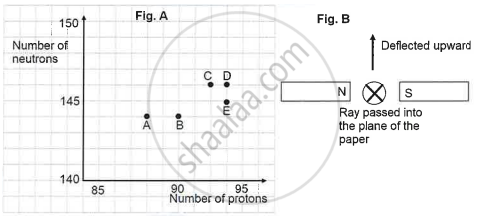
The graph (fig A) illustrates the correlation between the number of protons (x-axis) and the number of neutrons (y-axis) for elements A, B, C, D, and E in the periodic table. These elements are denoted by the letters rather than their conventional symbols. When the element C, depicted in the graph, undergoes radioactive decay, it releases radioactive rays. When these rays are directed into the plane of the paper in the presence of a magnetic field, as indicated in the fig B, they experience deflection, causing them to move upwards.
|
Name the law used to identify the radioactive radiation emitted by the element.