Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Obtain the binding energy of the nuclei `""_26^56"Fe"` and `""_83^209"Bi"` in units of MeV from the following data:
`"m"(""_26^56"Fe")` = 55.934939 u
`"m"(""_83^209"Bi")`= 208.980388 u
उत्तर
Atomic mass of `""_56^26"Fe"`, m1 = 55.934939 u
`""_56^26"Fe"` nucleus has 26 protons and (56 − 26) = 30 neutrons
Hence, the mass defect of the nucleus, Δm = 26 × mH + 30 × mn − m1
Where,
Mass of a proton, mH = 1.007825 u
Mass of a neutron, mn = 1.008665 u
∴ Δm = 26 × 1.007825 + 30 × 1.008665 − 55.934939
= 26.20345 + 30.25995 − 55.934939
= 0.528461 u
But 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2
∴ Δm = 0.528461 × 931.5 MeV/c2
The binding energy of this nucleus is given as:
Eb1 = Δmc2
Where,
c = Speed of light
∴ Eb1 = 0.528461 × 931.5 `(("MeV")/"c"^2) xx "c"^2`
= 492.26 MeV
Average binding energy per nucleon = `492.26/56` = 8.79 MeV
Atomic mass of `""_83^209"Bi"`, m2 = 208.980388 u
`""_83^209"Bi"` nucleus has 83 protons and (209 − 83) 126 neutrons.
Hence, the mass defect of this nucleus is given as:
Δm' = 83 × mH + 126 × mn − m2
Where,
Mass of a proton, mH = 1.007825 u
Mass of a neutron, mn = 1.008665 u
∴ Δm' = 83 × 1.007825 + 126 × 1.008665 − 208.980388
= 83.649475 + 127.091790 − 208.980388
= 1.760877 u
But 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2
∴ Δm' = 1.760877 × 931.5 MeV/c2
Hence, the binding energy of this nucleus is given as:
Eb2 = Δm'c2
= 1.760877 × 931.5 `(("MeV")/"c"^2) xx "c"^2`
= 1640.26 MeV
Average binding energy per nucleon = `1640.26/209` = 7.848 MeV
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive an expression for the total energy of electron in ‘n' th Bohr orbit. Hence show that energy of the electron is inversely proportional to the square of principal quantum number. Also define binding energy.
The neutron separation energy is defined as the energy required to remove a neutron from the nucleus. Obtain the neutron separation energies of the nuclei `""_20^41"Ca"` and `""_13^27 "Al"` from the following data:
`"m"(""_20^40"Ca")` = 39.962591 u
`"m"(""_20^41"Ca")` = 40.962278 u
`"m"(""_13^26"Al")` = 25.986895 u
`"m"(""_13^27"Al")` = 26.981541 u
What is the significance of binding energy per nucleon of a nucleus of a radioactive element?
Define half-life of a radioactive substance
Define the terms (i) half-life (T1/2) and (ii) average life (τ). Find out their relationships with the decay constant (λ).
If the nucleons of a nucleus are separated from each other, the total mass is increased. Where does this mass come from?
How much energy is released in the following reaction : 7Li + p → α + α.
Atomic mass of 7Li = 7.0160 u and that of 4He = 4.0026 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
Find the binding energy per nucleon of `""_79^197"Au"` if its atomic mass is 196.96 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
Calculate mass defect and binding energy per nucleon of `"_10^20 Ne`, given
Mass of `"_10^20 Ne= 19.992397` u
Mass of `"_0^1H = 1.007825` u
Mass of `"_0^1n = 1.008665` u
In a nuclear reactor, what is the function of:
(i) The moderator
(ii) The control rods
(iii) The coolant
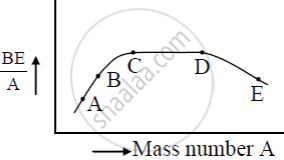
The figure shows the plot of binding energy (BE) per nucleon as a function of mass number A. The letters A, B, C, D, and E represent the positions of typical nuclei on the curve. Point out, giving reasons, the two processes (in terms of A, B, C, D, and E ), one of which can occur due to nuclear fission and the other due to nuclear fusion.
An electron in hydrogen atom stays in its second orbit for 10−8 s. How many revolutions will it make around the nucleus at that time?
In a periodic table the average atomic mass of magnesium is given as 24.312 u. The average value is based on their relative natural abundance on earth. The three isotopes and their masses are\[\ce{_12^24Mg}\](23.98504 u), \[\ce{_12^25Mg}\] (24.98584 u), and \[\ce{_12^26Mg}\] (25.98259 u). The natural abundance of \[\ce{_12^24Mg}\] is 78.99% by mass. Calculate the abundances of other two isotopes.
Determine the binding energy per nucleon of the americium isotope \[\ce{_95^244Am}\], given the mass of \[\ce{_95^244Am}\] to be 244.06428 u.
The difference in mass of a nucleus and its constituents is called ______.
A body's centre of mass
Mx and My denote the atomic masses of the parent and the daughter nuclei respectively in a radioactive decay. The Q-value for a β– decay is Q1 and that for a β+ decay is Q2. If m e denotes the mass of an electron, then which of the following statements is correct?
The deuteron is bound by nuclear forces just as H-atom is made up of p and e bound by electrostatic forces. If we consider the force between neutron and proton in deuteron as given in the form of a Coulomb potential but with an effective charge e′: F = `1/(4πε_0) e^('2)/r` estimate the value of (e’/e) given that the binding energy of a deuteron is 2.2 MeV.
What is meant by “binding energy per nucleon” of a nucleus?
