Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
On the basis of which evidences D-glucose was assigned the following structure?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CHO}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{(CHOH)4}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{CH2OH}
\end{array}\]
उत्तर
This structure was assigned on the basis of the following evidences:
1. Molecular formula: The molecular formula of glucose has been found to be \[\ce{C6H12O6}\].
2. Straight chain structure:
(i) When aqueous solution of glucose is treated with sodium amalgam (Na/Hg) or sodium borohydride, it is reduced to sorbitol (or glucitol) a hexahedric alcohol.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.}\ce{CHO}\phantom{.......................}\ce{CH2OH}\phantom{..}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{...........................}|\phantom{........}\\
\ce{(CHOH)4 + 2[H] ->[Na amalgam] (CHOH)4}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{...........................}|\phantom{........}\\\
\phantom{..}\ce{CH2OH}\phantom{....................}\ce{\underset{Sorbitol}{CH2OH}\phantom{....}}
\end{array}\]
(ii) Prolonged heating with hydriodic acid and red phosphorus at 100°C gives a mixture of n-hexane and 2-iodohexane.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{\underset{Glucose}{CH2OH(CHOH)4CHO} ->[Hl][red P, 100°C] \underset{n-hexane}{CH3(CH2)4CH3} + CH3CH(CH2)3CH3}\\
\phantom{............................................}|\\
\phantom{............................................}\ce{\underset{2-Iodohexane}{I}}
\end{array}\]
The formation of n-hexane suggests that all the six carbon atoms in glucose are arranged in a straight chain structure of glucose.
3. Presence of five hydroxyl (-OH) groups: On acetylation with acetic anhydride, glucose gives a pentaacetate. This confirms that glucose contains five –OH groups. We know that the presence of two or more –OH groups on the same carbon atom makes the molecules unstable. Now since glucose is a stable compound, therefore, the five -OH groups must present on different carbon atoms.
4. Presence of one primary alcoholic group: On oxidation with cone, nitric acid, both glucose and gluconic acid give the same dicarboxylic acid, saccharic acid or glucaric acid. The primary alcoholic group \[\ce{(CH2OH)}\] is always present at the end of the carbon chain.
5. Presence of an aldehyde (-CHO) group: Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine, \[\ce{NH2OH}\] to form glucose CHO oxime. Which suggest that glucose contains a carbonyl \[\ce{(CHOH)4}\] (>C = O) groups.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
What is the most abundant organic compound on earth?
Oxime is formed by treating glucose with ____________.
Which one of the following compounds is different from the rest?
Glucose does not react with ____________.
The number of chiral carbon atoms present in cyclic structure α-D(+) glucose:
Which one is correct?
Which of the following pairs represents anomers?
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
| (I) |  |
| (II) | 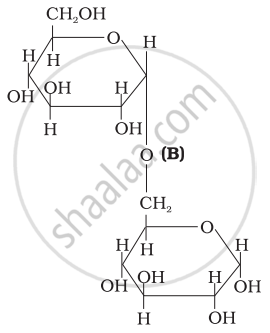 |
| (III) | 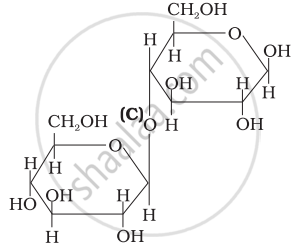 |
Account for the following:
What happens when D – glucose is treated with the following reagents
HNO3
