Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle is projected with a speed u at an angle θ with the horizontal. Consider a small part of its path near the highest position and take it approximately to be a circular arc. What is the radius of this circular circle? This radius is called the radius of curvature of the curve at the point.
उत्तर
At the highest point, the vertical component of velocity is zero.
So, at the highest point, we have:
velocity = v = ucosθ
Centripetal force on the particle = \[\frac{m v^2}{r}\]
\[\Rightarrow \frac{m v^2}{r} = \frac{m u^2 \cos^2 \theta}{r}\]
At the highest point, we have :
\[mg = \frac{m v^2}{r}\]
Here, r is the radius of curvature of the curve at the point.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A smooth block loosely fits in a circular tube placed on a horizontal surface. The block moves in a uniform circular motion along the tube. Which wall (inner or outer) will exert a nonzero normal contact force on the block?
A particle is kept fixed on a turntable rotating uniformly. As seen from the ground the particle goes in a circle, its speed is 20 cm/s and acceleration is 20 cm/s2. The particle is now shifted to a new position to make the radius half of the original value. The new value of the speed and acceleration will be
A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
The position vector of a particle in a circular motion about the origin sweeps out equal area in equal time. Its
(a) velocity remains constant
(b) speed remains constant
(c) acceleration remains constant
(d) tangential acceleration remains constant.
A particle is going in a spiral path as shown in figure with constant speed.
A ceiling fan has a diameter (of the circle through the outer edges of the three blades) of 120 cm and rpm 1500 at full speed. Consider a particle of mass 1 g sticking at the outer end of a blade. How much force does it experience when the fan runs at full speed? Who exerts this force on the particle? How much force does the particle exert on the blade along its surface?
A simple pendulum is suspended from the ceiling of a car taking a turn of radius 10 m at a speed of 36 km/h. Find the angle made by he string of the pendulum with the vertical if this angle does not change during the turn. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Suppose the bob of the previous problem has a speed of 1.4 m/s when the string makes an angle of 0.20 radian with the vertical. Find the tension at this instant. You can use cos θ ≈ 1 − θ2/2 and SINθ ≈ θ for small θ.
In non-uniform circular motion, the ratio of tangential to radial acceleration is (r = radius, a = angular acceleration and v = linear velocity)
A particle of mass m is performing UCM along a circle of radius r. The relation between centripetal acceleration a and kinetic energy E is given by
A wheel is subjected to uniform angular acceleration about its axis. The wheel is starting from rest and it rotates through an angle θ1, in first two seconds. In the next two seconds, it rotates through an angle θ2. The ratio θ1/θ2 is ____________.
A body is moving along a circular track of radius 100 m with velocity 20 m/s. Its tangential acceleration is 3 m/s2, then its resultant acceleration will be ______.
Angular displacement (θ) of a flywheel varies with time as θ = at + bt2 + ct3 then angular acceleration is given by ____________.
If a cyclist doubles his speed while negotiating a curve, how does the tendency to overturn vary?
An engine requires 5 seconds to go from a speed of 600 r.p.m. to 1200 r.p.m. How many revolutions does it make in this period?
A body is moving along a circular track of radius 100 m with velocity 20 m/s. Its tangential acceleration is 3 m/s2 then its resultant accelaration will be ______.
A racing car travels on a track (without banking) ABCDEFA (Figure). ABC is a circular arc of radius 2 R. CD and FA are straight paths of length R and DEF is a circular arc of radius R = 100 m. The co-efficient of friction on the road is µ = 0.1. The maximum speed of the car is 50 ms–1. Find the minimum time for completing one round.

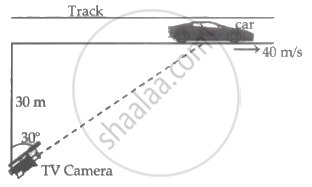
A racing car is travelling along a track at a constant speed of 40 m/s. A T.V. cameraman is recording the event from a distance of 30 m directly away from the track as shown in the figure. In order to keep the car under view in the position shown, the angular speed with which the camera should be rotated is ______.