Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
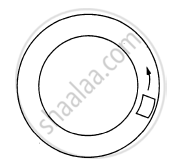
A smooth block loosely fits in a circular tube placed on a horizontal surface. The block moves in a uniform circular motion along the tube. Which wall (inner or outer) will exert a nonzero normal contact force on the block?
उत्तर
The outer wall will exert a non-zero normal contact force on the block. As the block moves in a uniform circular motion, centrifugal force in radially outward direction acts on it and it comes in contact with the outer wall of the tube.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Tow cars having masses m1 and m2 moves in circles of radii r1 and r2 respectively. If they complete the circle in equal time, the ratio of their angular speed ω1/ω2 is
A particle is kept fixed on a turntable rotating uniformly. As seen from the ground the particle goes in a circle, its speed is 20 cm/s and acceleration is 20 cm/s2. The particle is now shifted to a new position to make the radius half of the original value. The new value of the speed and acceleration will be
A coin placed on a rotating turntable just slips. If it is placed at a distance of 4 cm from the centre. If the angular velocity of the turntable is doubled, it will just slip at a distance of
A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
A train A runs from east to west and another train B of the same mass runs from west to east at the same speed along the equator. A presses the track with a force F1 and B presses the track with a force F2.
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
Find the acceleration of the moon with respect to the earth from the following data:
Distance between the earth and the moon = 3.85 × 105 km and the time taken by the moon to complete one revolution around the earth = 27.3 days.
A motorcycle has to move with a constant speed on an over bridge which is in the form of a circular arc of radius R and has a total length L. Suppose the motorcycle starts from the highest point.(a) What can its maximum velocity be for which the contact with the road is not broken at the highest point? (b) If the motorcycle goes at speed 1/√2 times the maximum found in part (a), where will it lose the contact with the road? (c) What maximum uniform speed can it maintain on the bridge if it does not lose contact anywhere on the bridge?
A block of mass m is kept on a horizontal ruler. The friction coefficient between the ruler and the block is μ. The ruler is fixed at one end and the block is at a distance L from the fixed end. The ruler is rotated about the fixed end in the horizontal plane through the fixed end. (a) What can the maximum angular speed be for which the block does not slip? (b) If the angular speed of the ruler is uniformly increased from zero at an angular acceleration α, at what angular speed will the block slip?
A hemispherical bowl of radius R is rotated about its axis of symmetry which is kept vertical. A small block is kept in the bowl at a position where the radius makes an angle θ with the vertical. The block rotates with the bowl without any slipping. The friction coefficient between the block and the bowl surface is μ. Find the range of the angular speed for which the block will not slip.
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
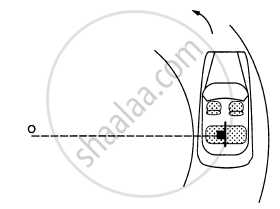
A table with smooth horizontal surface is placed in a circle of a large radius R (In the following figure). A smooth pulley of small radius is fastened to the table. Two masses m and 2m placed on the table are connected through a string going over the pulley. Initially the masses are held by a person with the string along the outward radius and then the system is released from rest (with respect to the cabin). Find the magnitude of the initial acceleration of the masses as seen from the cabin and the tension in the string.
Choose the correct option.
Consider the following cases:
(P) A planet revolving in an elliptical orbit.
(Q) A planet revolving in a circular orbit.
Principle of conservation of angular momentum comes in force in which of these?
A particle of mass m is performing UCM along a circle of radius r. The relation between centripetal acceleration a and kinetic energy E is given by
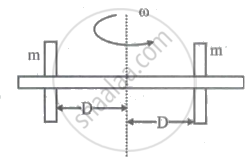
Two identical masses are connected to a horizontal thin (massless) rod as shown in the figure. When their distance from the pivot is D, a torque τ produces an angular acceleration of α1. The masses are now repositioned so that they are 2D from the pivot. The same torque produces an angular acceleration α2 which is given by ______
An engine requires 5 seconds to go from a speed of 600 r.p.m. to 1200 r.p.m. How many revolutions does it make in this period?
An engine is moving on a c1rcular path of radius 200 m with speed of 15 m/s. What will be the frequency heard by an observer who is at rest at the centre of the circular path, when engine blows the whistle with frequency 250 Hz?
When a body slides down from rest along a smooth inclined plane making an angle of 45° with the horizontal, it takes time T. When the same body slides down from rest along a rough inclined plane making the same angle and through the same distance, it is seen to take time pT, where p is some number greater than 1. Calculate the co-efficient of friction between the body and the rough plane.
A racing car travels on a track (without banking) ABCDEFA (Figure). ABC is a circular arc of radius 2 R. CD and FA are straight paths of length R and DEF is a circular arc of radius R = 100 m. The co-efficient of friction on the road is µ = 0.1. The maximum speed of the car is 50 ms–1. Find the minimum time for completing one round.

Find the angular acceleration of a particle in circular motion which slows down from 300 r.p.m. to 0 r.p.m. in 20 s.
