Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose a charge +Q1 is given to the positive plate and a charge −Q2 to the negative plate of a capacitor. What is the "charge on the capacitor"?
उत्तर
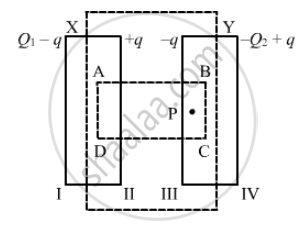
Given :
Charge on the positive plane = `+Q_1`
Charge on the negative plate = `-Q_2`
To calculate: Charge on the capacitor
Let ABCD be the Gaussian surface such that faces AD and BC lie inside plates X and Y, respectively.
Let q be the charge appearing on surface II. Then, the distribution of the charges on faces I, III and IV will be in accordance with the figure.
Let the area of the plates be A and the permittivity of the free space be `∈_0`.
Now, to determine q in terms of Q1 and Q2, we need to apply Gauss's law to calculate the electric field due to all four faces of the capacitor at point P. Also, we know that the electric field inside a capacitor is zero.
Electric field due to face I at point P, E1 = `(Q_1 - q)/(2∈_0A)`
Electric field due to face II at point P, E2= `(+q)/(2∈_0A)`
Electric field due to face III at point P, E3 = `(-q)/{2∈_0A)`
Electric field due to face IV at point P, E4 = `-((-Q_2+q)/(2∈_0A))` (Negative sign is used as point P lies on the LHS of face IV.)
Since point P lies inside the conductor,
E1 + E2 + E3 + E4 = 0
`therefore` `Q_1-q+q-q-(-Q_2+q)` = 0
⇒ q = `(Q_1+Q_2)/2`
Thus , the change on the capacitor is `(Q_1+Q_2)/2`, which is the charge on faces II and III.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two capacitors of unknown capacitances C1 and C2 are connected first in series and then in parallel across a battery of 100 V. If the energy stored in the two combinations is 0.045 J and 0.25 J respectively, determine the value of C1 and C2. Also calculate the charge on each capacitor in parallel combination.
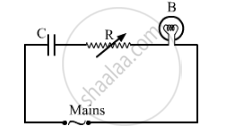
A capacitor 'C', a variable resistor 'R' and a bulb 'B' are connected in series to the ac mains in circuit as shown. The bulb glows with some brightness. How will the glow of the bulb change if (i) a dielectric slab is introduced between the plates of the capacitor, keeping resistance R to be the same; (ii) the resistance R is increased keeping the same capacitance?
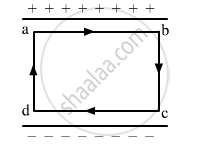
The electric field inside a parallel plate capacitor is E. Find the amount of work done in moving a charge q over a closed loop a b c d a.
Three capacitors of capacitances 2 pF, 3 pF and 4 pF are connected in parallel. Determine the charge on each capacitor if the combination is connected to a 100 V supply.
An electrical technician requires a capacitance of 2 µF in a circuit across a potential difference of 1 kV. A large number of 1 µF capacitors are available to him each of which can withstand a potential difference of not more than 400 V. Suggest a possible arrangement that requires the minimum number of capacitors.
The plates of a parallel-plate capacitor are given equal positive charges. What will be the potential difference between the plates? What will be the charges on the facing surfaces and on the outer surfaces?
If the capacitors in the previous question are joined in parallel, the capacitance and the breakdown voltage of the combination will be
A parallel-plate capacitor having plate area 25 cm2 and separation 1⋅00 mm is connected to a battery of 6⋅0 V. Calculate the charge flown through the battery. How much work has been done by the battery during the process?
The plates of a capacitor are 2⋅00 cm apart. An electron-proton pair is released somewhere in the gap between the plates and it is found that the proton reaches the negative plate at the same time as the electron reaches the positive plate. At what distance from the negative plate was the pair released?
A capacitor of capacitance 5⋅00 µF is charged to 24⋅0 V and another capacitor of capacitance 6⋅0 µF is charged to 12⋅0 V. (a) Find the energy stored in each capacitor. (b) The positive plate of the first capacitor is now connected to the negative plate of the second and vice versa. Find the new charges on the capacitors. (c) Find the loss of electrostatic energy during the process. (d) Where does this energy go?
Three capacitors of capacitance `C_1 = 3muf` , `C_2 = 6muf` , `C_3 = 10muf` , are connected to a 10V battery as shown in figure 3 below :
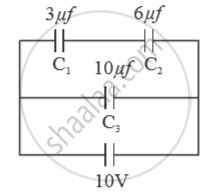
Calculate :
(a) Equivalent capacitance.
(b) Electrostatic potential energy stored in the system
An ac circuit consists of a series combination of circuit elements X and Y. The current is ahead of the voltage in phase by `pi /4` . If element X is a pure resistor of 100Ω ,
(a) name the circuit element Y.
(b) calculate the rms value of current, if rms value of voltage is 141V.
(c) what will happen if the ac source is replaced by a dc source ?
A wire of resistance 'R' is cut into 'n' equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel with each other. The equivalent resistance of the combination is :
An ac circuit consists of a series combination of circuit elements X and Y. The current is ahead of the voltage in phase by `pi/4`. If element X is a pure resistor of 100 Ω,
(a) name the circuit element Y.
(b) calculate the rms value of current, if rms of voltage is 141 V.
(c) what will happen if the ac source is replaced by a dc source
Three different capacitors are·connected in series. Then:-
Two charges q1 and q2 are placed at (0, 0, d) and (0, 0, – d) respectively. Find locus of points where the potential a zero.
