Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Sometimes it is said that "heat is developed" in a resistance when there is an electric current in it. Recall that heat is defined as the energy being transferred due to temperature difference. Is the statement in quotes technically correct?
उत्तर
Yes, the given statement is correct. When charge flows through a conductor, its electric potential energy decreases. This loss in electric potential energy appears as increased heat energy of the resistor. Thus, heat energy is developed in a resistor when there is an electric current in it.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
At room temperature (27.0°C) the resistance of a heating element is 100 Ω. What is the temperature of the element if the resistance is found to be 117 Ω, given that the temperature coefficient of the material of the resistor is 1.70 × 10−4 °C−1.
Draw labelled graphs to show how electrical resistance varies with temperature for:
1) a metallic wire.
2) a piece of carbon
Consider a circuit containing an ideal battery connected to a resistor. Do "work done by the battery" and "the thermal energy developed" represent two names of the same physical quantity?
The resistance of an iron wire and a copper wire at 20°C are 3.9 Ω and 4.1 Ω, respectively. At what temperature will the resistance be equal? Temperature coefficient of resistivity for iron is 5.0 × 10–3 K–1 and for copper, it is 4.0 × 10–3 K–1. Neglect any thermal expansion.
When a current passes through a resistor, its temperature increases. Is it an adiabatic process?
Is neutral temperature always the arithmetic mean of the inversion temperature and the temperature of the cold junction? Does the unit of temperature have an effect in deciding this question?
As temperature increases, the viscosity of liquids decreases considerably. Will this decrease the resistance of an electrolyte as the temperature increases?
The constants a and b for the pair silver-lead are 2.50 μV°C−1 and 0.012μV°C−2, respectively. For a silver-lead thermocouple with colder junction at 0°C, ______________ .
(a) there will be no neutral temperature
(b) there will be no inversion temperature
(c) there will not be any thermo-emf even if the junctions are kept at different temperatures
(d) there will be no current in the thermocouple even if the junctions are kept at different temperatures
An electric kettle used to prepare tea, takes 2 minutes to boil 4 cups of water (1 cup contains 200 cc of water) if the room temperature is 25°C. (a) If the cost of power consumption is Re 1.00 per unit (1 unit = 1000 watt-hour), calculate the cost of boiling 4 cups of water. (b) What will be the corresponding cost if the room temperature drops to 5°C?
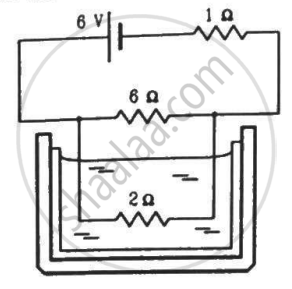
The 2.0 Ω resistor shown in the figure is dipped into a calorimeter containing water. The heat capacity of the calorimeter together with water is 2000 J K−1. (a) If the circuit is active for 15 minutes, what would be the rise in the temperature of the water? (b) Suppose the 6.0 Ω resistor gets burnt. What would be the rise in the temperature of the water in the next 15 minutes?
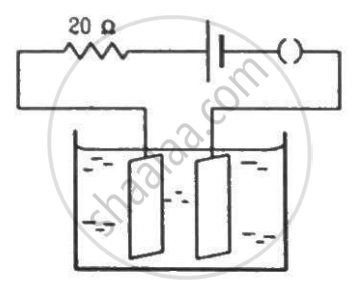
The figure shows an electrolyte of AgCl through which a current is passed. It is observed that 2.68 g of silver is deposited in 10 minutes on the cathode. Find the heat developed in the 20 Ω resistor during this period. Atomic weight of silver is 107.9 g/mol−1.
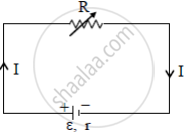
A variable resistor R is connected across a cell of emf ε and internal resistance r as shown in the figure. Draw a plot showing the variation of
(i) Terminal voltage V and
(ii) the current I, as a function of R.
An electrical cable of copper has just one wire of radius 9 mm. Its resistance is 5 ohm. This single copper wire of the cable is replaced by 6 different well insulated copper wires each of radius 3 mm. The total resistance of the cable will now be equal to ______.
The higher and lower fixed points on a thermometer are separated by 160 mm. When the length of the mercury thread above the lower point is 40 mm, the temperature reading would be :
The specific resistance of all the metals is the most affected by ______
