Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the basic proportionality theorem.
उत्तर
If a line is draw parallel to one side of a triangle intersect the other two sides, then it divides the other two sides in the same ratio.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = 6 cm, DB = 9 cm and AE = 8 cm, find AC.
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If `"AD"/"DB"=2/3` and AC = 18 cm, find AE
In ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively such that DE || BC
If AD = 8cm, AB = 12 cm and AE = 12 cm, find CE.
In a ΔABC, D and E are points on the sides AB and AC respectively. For the following case show that DE || BC
AB = 10.8 cm, BD = 4.5 cm, AC = 4.8 cm and AE = 2.8 cm.
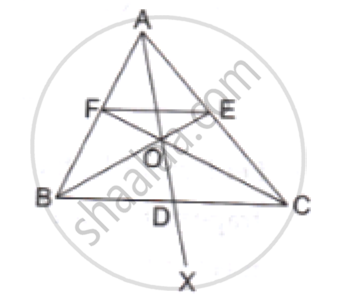
In three line segments OA, OB, and OC, points L, M, N respectively are so chosen that LM || AB and MN || BC but neither of L, M, N nor of A, B, C are collinear. Show that LN ||AC.
ΔABC and ΔDBC lie on the same side of BC, as shown in the figure. From a point P on BC, PQ||AB and PR||BD are drawn, meeting AC at Q and CD at R respectively. Prove that QR||AD.
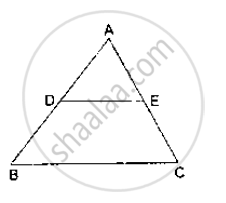
In the adjoining figure, ABC is a triangle in which AB = AC. IF D and E are points on AB and AC respectively such that AD = AE, show that the points B, C, E and D are concyclic.
Find the length of each side of a rhombus whose diagonals are 24cm and 10cm long.
In the given figure, D is the midpoint of side BC and AE⊥BC. If BC = a, AC = b, AB = c, AD = p and AE = h, prove that
(i)`B^2=p^2+ax+a^2/x`
(ii)` c^2=p^2-ax+a^2/x`
(iii) `b^2+c^2=2p^2+a^2/2`
(iv)`b^2-c^2=2ax`

ABC is an isosceles triangle, right-angled at B. Similar triangles ACD and ABE are constructed on sides AC and AB. Find the ratio between the areas of ΔABE and ΔACD.