Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The average energy per molecule is proportional to ______
विकल्प
the pressure of the gas
the volume of the gas
the absolute temperature of the gas
the mass of the gas
उत्तर
The average energy per molecule is proportional to the absolute temperature of the gas.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Molar volume is the volume occupied by 1 mol of any (ideal) gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP: 1 atmospheric pressure, 0 °C). Show that it is 22.4 litres
An oxygen cylinder of volume 30 litres has an initial gauge pressure of 15 atm and a temperature of 27 °C. After some oxygen is withdrawn from the cylinder, the gauge pressure drops to 11 atm and its temperature drops to 17 °C. Estimate the mass of oxygen taken out of the cylinder (R = 8.31 J mol–1 K–1, molecular mass of O2 = 32 u)
Three vessels of equal capacity have gases at the same temperature and pressure. The first vessel contains neon (monatomic), the second contains chlorine (diatomic), and the third contains uranium hexafluoride (polyatomic).
Is the root mean square speed of molecules the same in the three cases? If not, in which case is vrms the largest?
At what temperature is the root mean square speed of an atom in an argon gas cylinder equal to the rms speed of a helium gas atom at – 20 °C? (atomic mass of Ar = 39.9 u, of He = 4.0 u).
During the practical session in the lab when hydrogen sulphide gas having offensive odour is prepared for some test, we can smell the gas even 50 metres away. Explain the phenomenon.
What is diffusion? Give an example to illustrate it.
Give reasons for the following:
Gas fills the vessel completely in which it is kept.
Match the following:
|
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) |
cm3 |
(i) Pressure |
|
(b) |
Kelvin |
(ii) Temperature |
|
(c) |
Torr |
(iii) Volume |
|
(d) |
Boyle's law |
(iv) `"V"/"T" = ("V"_1)/("T"_1)` |
|
(a) |
Charles's law |
(v) `"PV"/"T" = ("P"_1 "V"_1)/"T"_1` |
|
|
|
(vi) PV = P1V1 |
Correct the following statement:
0°C is equal to zero Kelvin.
Name or state the following:
The absolute temperature value corresponding to 35°C.
Give reason for the following:
Temperature remaining constant the product of the vol. & the press, of a given mass of dry gas is a constant.
Give reason for the following:
Volumes of gases are converted into s.t.p. conditions and then compared.
Show that for monoatomic gas the ratio of the two specific heats is 5:3.
Gases exert pressure on the walls of the container because the gas molecules ______
The equation of state for 2g of oxygen at a pressure 'P' and temperature 'T', when occupying a volume 'V' will be ______.
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at room temperature (27 °C).
Which of the following diagrams (Figure) depicts ideal gas behaviour?
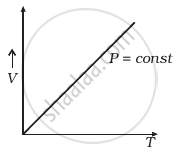 (a) |
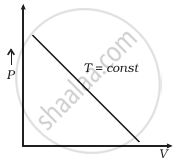 (b) |
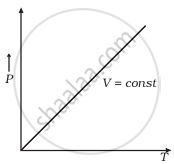 (c) |
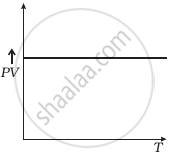 (d) |
Calculate the number of atoms in 39.4 g gold. Molar mass of gold is 197g mole–1.
A box of 1.00 m3 is filled with nitrogen at 1.50 atm at 300K. The box has a hole of an area 0.010 mm2. How much time is required for the pressure to reduce by 0.10 atm, if the pressure outside is 1 atm.
The volume V of an enclosure contains a mixture of three gases, 16 g of oxygen, 28 g of nitrogen and 44 g of carbon dioxide at absolute temperature T. Consider R as universal gas constant. The pressure of the mixture of gases is ______.
Cooking gas containers are kept in a lorry moving with uniform speed. The temperature of the gas molecules inside will ______.
For a wave, y = 0.0002 sin`[2pi(110"t"-x/3)+pi/3]` is travelling in a medium. The energy per unit volume being transferred by wave if density of medium is 1.5 kg/m3, is ______.
Two tanks of equal volume contain equal mass of oxygen and nitrogen at 127°C. Find the ratio of pressure in two tanks.
