Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The electric field associated with a monochromatic beam is 1.2 × 1015 times per second. Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons when this light falls on a metal surface whose work function is 2.0 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
उत्तर
Given :-
Electric field of the monochromatic beam, `E = 1.2 xx 10^15` times per second
Frequency, v = `(1.2 xx 10^15)/2 = 0.6 xx 10^15 "Hz"`
Work function of the metal surface, `phi` = 2.0 eV
From Einstein's photoelectric equation, kinetic energy,
`K = hv - phi_0`
`⇒ K = (6.63 xx 10^-34 xx 0.6 xx 10^15)/(1.6 xx 10^-19) - 2`
`= 0.486 "eV"`
Thus, the maximum kinetic energy of a photon is 0.486 eV.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A mercury lamp is a convenient source for studying frequency dependence of photoelectric emission, since it gives a number of spectral lines ranging from the UV to the red end of the visible spectrum. In our experiment with rubidium photo-cell, the following lines from a mercury source were used:
λ1 = 3650 Å, λ2 = 4047 Å, λ3 = 4358 Å, λ4 = 5461 Å, λ5 = 6907 Å,
The stopping voltages, respectively, were measured to be:
V01 = 1.28 V, V02 = 0.95 V, V03 = 0.74 V, V04 = 0.16 V, V05 = 0 V
Determine the value of Planck’s constant h, the threshold frequency and work function for the material.
[Note: You will notice that to get h from the data, you will need to know e (which you can take to be 1.6 × 10−19 C). Experiments of this kind on Na, Li, K, etc. were performed by Millikan, who, using his own value of e (from the oil-drop experiment) confirmed Einstein’s photoelectric equation and at the same time gave an independent estimate of the value of h.]
Every metal has a definite work function. Why do all photoelectrons not come out with the same energy if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photoelectrons?
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
When the sun is directly overhead, the surface of the earth receives 1.4 × 103 W m−2 of sunlight. Assume that the light is monochromatic with average wavelength 500 nm and that no light is absorbed in between the sun and the earth's surface. The distance between the sun and the earth is 1.5 × 1011 m. (a) Calculate the number of photons falling per second on each square metre of earth's surface directly below the sun. (b) How many photons are there in each cubic metre near the earth's surface at any instant? (c) How many photons does the sun emit per second?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A 100 W light bulb is placed at the centre of a spherical chamber of radius 20 cm. Assume that 60% of the energy supplied to the bulb is converted into light and that the surface of the chamber is perfectly absorbing. Find the pressure exerted by the light on the surface of the chamber.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected when light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a cesium surface. Work function of cesium = 1.9 eV
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The work function of a photoelectric material is 4.0 eV. (a) What is the threshold wavelength? (b) Find the wavelength of light for which the stopping potential is 2.5 V.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A small piece of cesium metal (φ = 1.9 eV) is kept at a distance of 20 cm from a large metal plate with a charge density of 1.0 × 10−9 C m−2 on the surface facing the cesium piece. A monochromatic light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on the cesium piece. Find the minimum and maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons reaching the large metal plate. Neglect any change in electric field due to the small piece of cesium present.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Define the term: threshold frequency
Answer the following question.
Plot a graph of photocurrent versus anode potential for radiation of frequency ν and intensities I1 and I2 (I1 < I2).
Define the terms "stopping potential' and 'threshold frequency' in relation to the photoelectric effect. How does one determine these physical quantities using Einstein's equation?
In photoelectric effect the photo current ______.
The graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal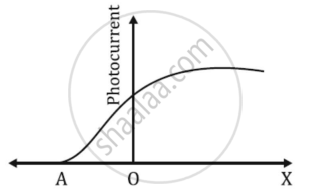
- What does X and A on the horizontal axis represent?
- Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation ʋ1, ʋ2 and ʋ3 (ʋ3 > ʋ2 > ʋ1) for the same intensity.
- Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I3 > I2 > I1) having the same frequency.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
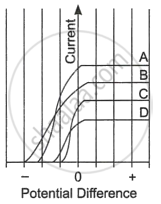
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
- Assertion (A): For the radiation of a frequency greater than the threshold frequency, the photoelectric current is proportional to the intensity of the radiation.
- Reason (R): Greater the number of energy quanta available, the greater the number of electrons absorbing the energy quanta and the greater the number of electrons coming out of the metal.
What is the effect of threshold frequency and stopping potential on increasing the frequency of the incident beam of light? Justify your answer.
