Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The electrons are emitted in the photoelectric effect from a metal surface.
विकल्प
only if the frequency of radiation is above a certain threshold value.
only if the temperature of the surface is high.
at the that is independent of the nature of metal.
with a maximum velocity proportional to the frequency of incident radiation
उत्तर
The electrons are emitted in the photoelectric effect from a metal surface only if the frequency of radiation is above a certain threshold value.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct option.
Polychromatic (containing many different frequencies) radiation is used in an experiment on the photoelectric effect. The stopping potential ______.
Explain the inverse linear dependence of stopping potential on the incident wavelength in a photoelectric effect experiment.
Using the values of work function given in the following table, tell which metal will require the highest frequency of incident radiation to generate photocurrent.
Typical values of work function for some common metals
| Metal | Work function (in eV) |
| Potassium | 2.3 |
| Sodium | 2.4 |
| Calcium | 2.9 |
| Zinc | 3.6 |
| Silver | 4.3 |
| Aluminium | 4.3 |
| Tungsten | 4.5 |
| Copper | 4.7 |
| Nickel | 5.0 |
| Gold | 5.1 |
The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons depends only on ______
Planck's constant is 6.6 × 10-34 Js. The momentum of each photon is given radiation Is 3.3 × 10-29 kg/s. The λ of radiation is ______.
State Einstein photoelectric equation. Explain 2 characteristics of the photoelectric effect on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
State Einstein’s photoelectric equation. Explain all characteristics of the photoelectric effect, on the basis of Einstein’s photoelectric equation.
The maximum velocity of the photoelectron emitted by the metal surface is v. Charge and the mass of the photoelectron is denoted by e and m, respectively. The stopping potential in volt is ______.
The energy of the incident photon on the metal surface is 3 W and then 5 W, where W is the work function for that metal. The ratio of velocities of emitted photoelectrons is ______.
The kinetic energy of the most energetic photoelectron emitted from a metal surface is doubled when the wavelength of the incident radiation is reduced from λ1 to λ2. The work function of the metal is ______
Which one of the following is TRUE in photoelectric emission?
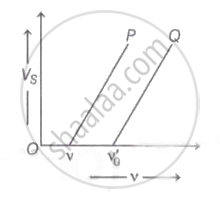
The graph of stopping potential `"V"_"s"` against frequency v of incident radiation is plotted for two different metals P and Q as shown in the graph. ΦP and ΦQ are work-functions of P and Q respectively, then
When light falls on a metal surface, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons depends upon ______
A metal surface is illuminated by light of given intensity and frequency to cause photoemission. If the intensity of illumination is reduced to one-fourth of its original value then the maximum KE of the emitted photoelectrons would be ______.
Light of frequency 2 times the threshold frequency is incident on a photo sensitive material. If the frequency is made `1/3`rd and intensity is doubled then the photocurrent will ______.
The work function of a substance is 4.0 eV. The longest wavelength of light that can cause photo-emission from this substance is approximately (h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js)[1eV = 1.6 × 10-19 J]
Following graphs show the variation of stopping potential corresponding to the frequency of incident radiation (F) for a given metal. The correct variation is shown in graph (v0 = Threshold frequency).
The lowest frequency of light that will cause the emission of photoelectrons from the surface of a metal (for which work function is 1.65 eV) will be ____________.
Which one of the following statements ts INCORRECT for stopping potential in photoelectric emission?
When light of wavelength '`lambda`' is incident on photosensitive surface, photons of power 'P' are emitted. The number of photons (n) emitted in 't' second is (h = Planck's constant, c = velocity of light in vacuum) ____________.
When the work function of a metal increases, maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons ____________.
The stopping potential in the context of photoelectric effect depends on the following property of incident electromagnetic radiation ______.
When radiation of wavelength λ is used to illuminate a metallic surface, the stopping potential is V. When the same surface is illuminated with radiation of wavelength 3λ, the stopping potential is `"V"/4`. If the threshold wavelength for the metallic surface is nλ. then value of n will be ______.
A point isotropic light source of power P = 12 watts is located on the axis of a circular mirror of radius R = 3 cm. If the distance of the source from the centre of the mirror is a = 39 cm and the reflection coefficient of the mirror is α = 0.70 then the force exerted by the light ray on the mirror is ______ × 10-10 N.
In a photocell, frequency of incident radiation is increased by keeping other factors constant (v > v0), the stopping potential ______.
Define photoelectric work function of a metal.
